Discover the top trends reshaping the banking landscape in 2024.
The banking industry is swiftly adapting to technological changes, eagerly implementing the latest available tech, including AI and especially GenAI-based tools. They are actively embracing these innovations to elevate customer experiences, streamline operations, and stay ahead in the competitive landscape. Below are key banking technology trends expected to shape the industry in 2024.
Artificial intelligence and advanced analytics
AI and machine learning have become integral to banking. Financial companies already used AI chatbots and virtual assistants to improve customer service, and now they’ve been increasingly employing GenAI to make these tools even more powerful, versatile, and natural-sounding. AI is also being used for fraud detection, client advisory, financial planning, trading, and risk management.
In general, in 2024, more banking processes will shift from rules-based systems to AI-based systems. Advanced analytics provides actionable insights from customer data. This enables banks to provide personalized services, predict customer needs, and streamline operations.
- Banks will use machine learning algorithms to draw deeper insights from large volumes of structured and unstructured data. This allows hyper-personalization of banking products to individual customers.
- Banks are deploying computer vision, video analytics, and sentiment analysis to assess customer emotions, gain feedback, and understand needs during interactions at branches or contact centers.
- Risk modeling and fraud detection will increasingly rely on advanced AI techniques like neural networks, deep learning, and natural language processing to spot anomalies and patterns in real time. This will enhance risk management.
- AI will be used to analyze earnings calls, executives’ public statements, economic data, news, etc., and generate investment recommendations for wealth management clients. This facilitates more informed decision-making.
- Intelligent process automation, combining AI with RPA, will automate more complex workflows that involve skill and judgment, like loan underwriting. This will improve efficiency and standardization.
- Analytics and predictive modeling will enable more accurate credit risk analysis, customer default prediction, expected loan losses, and optimal interest rates.
- AI techniques like reinforcement learning allow banks to dynamically optimize recommendations to customers across channels to improve cross-selling and upselling.
GenAI and LLMs deserve a separate mention here. While still a relatively new technology, it is rapidly gaining traction with significant potential to transform the financial industry. Here are some key ways banks will be using GenAI in 2024 and beyond:
- Personalized financial insights. As mentioned, AI tools can analyze vast amounts of customer data, but LLMs can also generate elaborate personalized reports and recommendations on spending habits, budgeting, and saving goals quickly.
- Enhanced conversational interfaces. Banks are developing chatbots powered by GenAI to answer customer questions, provide support, and even conduct simple transactions, offering a more natural and efficient way to interact.
- Improved accessibility. GenAI can be used to create summaries of complex financial documents or translate information into different languages, making banking services more accessible to a wider audience.
- Automated tasks. GenAI can automate repetitive back-office tasks like generating reports and summarizing data. It can also offer sound advice to clients regarding simple matters, thus freeing up human employees to focus on more complex tasks.
- Streamlined workflows. GenAI can optimize workflows by analyzing performance data and suggesting improvements to processes, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
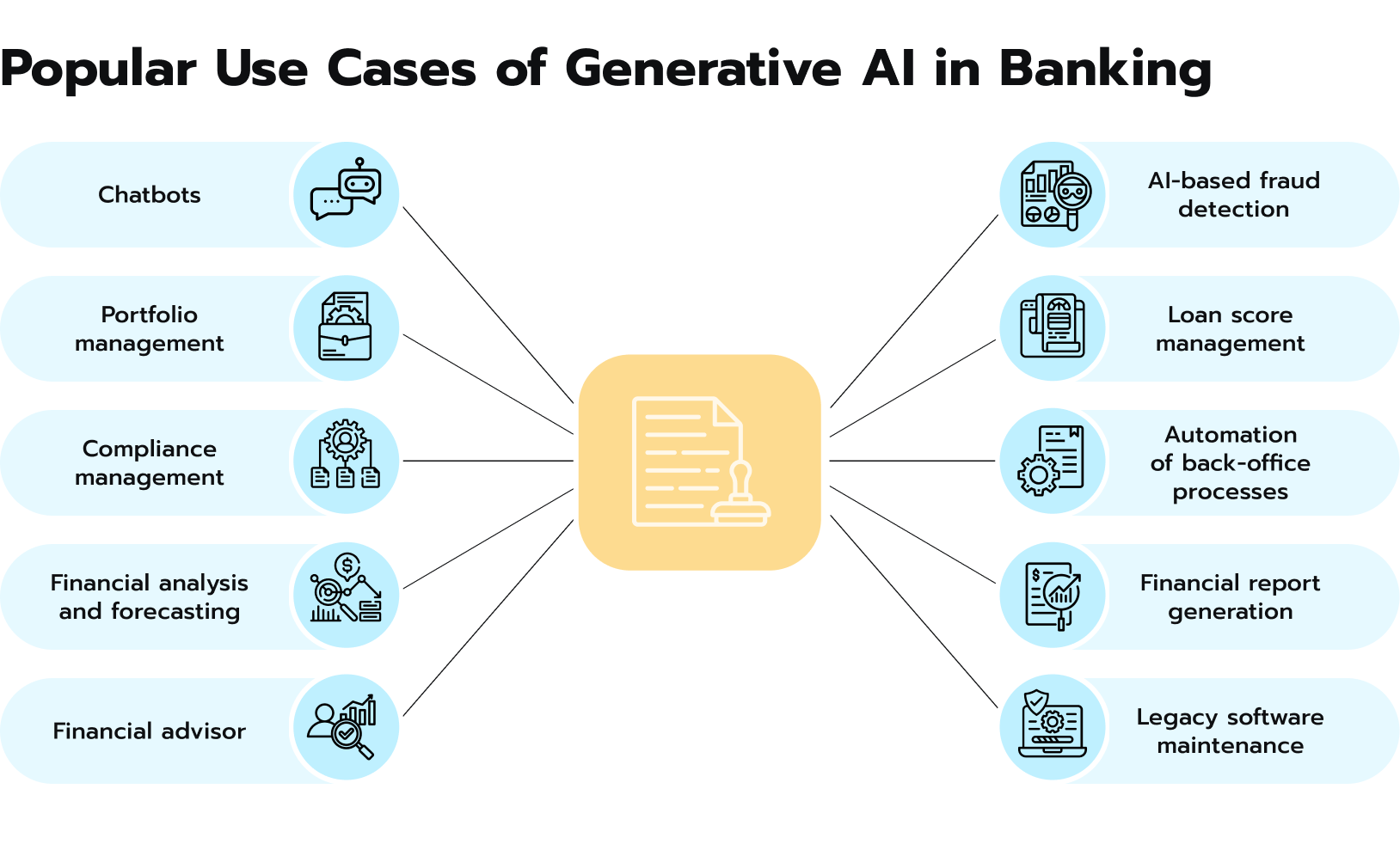 Fig 1. GenAI in banking.
Fig 1. GenAI in banking.
Banking automation trends
Automation will continue transforming how banks operate and deliver services. Banks are automating manual processes using technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic process automation. This improves speed and accuracy and allows banks to offer 24/7 services.
According to McKinsey, 75 to 80 percent of transactional operations (e.g., general accounting operations, payments processing) and up to 40 percent of more strategic activities (e.g., financial controlling and reporting, financial planning and analysis, treasury) can be automated. Overall, banks are expected to leverage automation to optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance both customer and employee experiences.
- Robotic process automation (RPA) will become more widespread in banking operations to automate repetitive, rules-based tasks. RPA can help banks improve efficiency, reduce costs, and achieve higher accuracy in processes like loan processing, customer onboarding, regulatory reporting, etc.
- Banks will increase their use of intelligent process automation, which combines RPA with AI and machine learning. This allows more complex processes that involve judgment and subjectivity to be automated.
- More banking processes will shift from legacy systems to automated cloud-based systems. Cloud enables banks to quickly scale capabilities, accelerate deployment of applications, and achieve faster time-to-market.
- Increased integration of application programming interfaces (APIs) will allow smoother data exchange and connectivity between banking systems and third parties like fintechs. This opens the door for embedded banking services.
- Automation will be used to help banks comply with regulations in areas like KYC and AML. AI can be used to automatically collect, verify, and update customer KYC information.
- Natural language processing and sentiment analysis will be used to understand call center conversations, analyze customer feedback, and better assess satisfaction levels.
- Banks will continue to digitize more back-end processes, including credit underwriting and decisioning, data processing, transaction reconciliation, etc., through automation and AI. This will improve efficiency and risk management.
DORA preparations
Financial firms across Europe are gearing up for the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), a new regulation that aims to bolster their resilience against operational disruptions, particularly cyber threats. Here’s a breakdown of the key preparation strategies financial companies will be enacting this year.
Gap analysis and roadmapping. Financial organizations are conducting gap analyses to identify areas where their current practices fall short of DORA’s requirements. This will help them develop roadmaps outlining the steps needed to establish a robust operational resilience framework.
IT risk management. DORA emphasizes a proactive approach to IT risk management. To meet the new demands, banks are:
- implementing robust policies and procedures to identify, assess, and mitigate potential IT threats utilizing advanced security tools to scan their digital landscape for vulnerabilities and design effective mitigation strategies
- conducting penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and resilience scenario simulations to identify and address weaknesses before they become critical.
Third-party risk management (TPRM). Since many firms rely on third-party vendors for critical services, DORA necessitates ensuring these vendors also comply with its regulations. This might involve:
- renegotiating contracts to include DORA compliance clauses
- implementing stricter vendor selection criteria based on their cybersecurity posture
- conducting regular assessments of their third-party vendors’ compliance with DORA.
Investment and upskilling. Meeting DORA’s requirements often necessitates investments in:
- governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) frameworks for ICT, cyber, and TPRM functions, advanced security tools and technologies
- training and upskilling employees on DORA’s requirements and best practices for operational resilience.
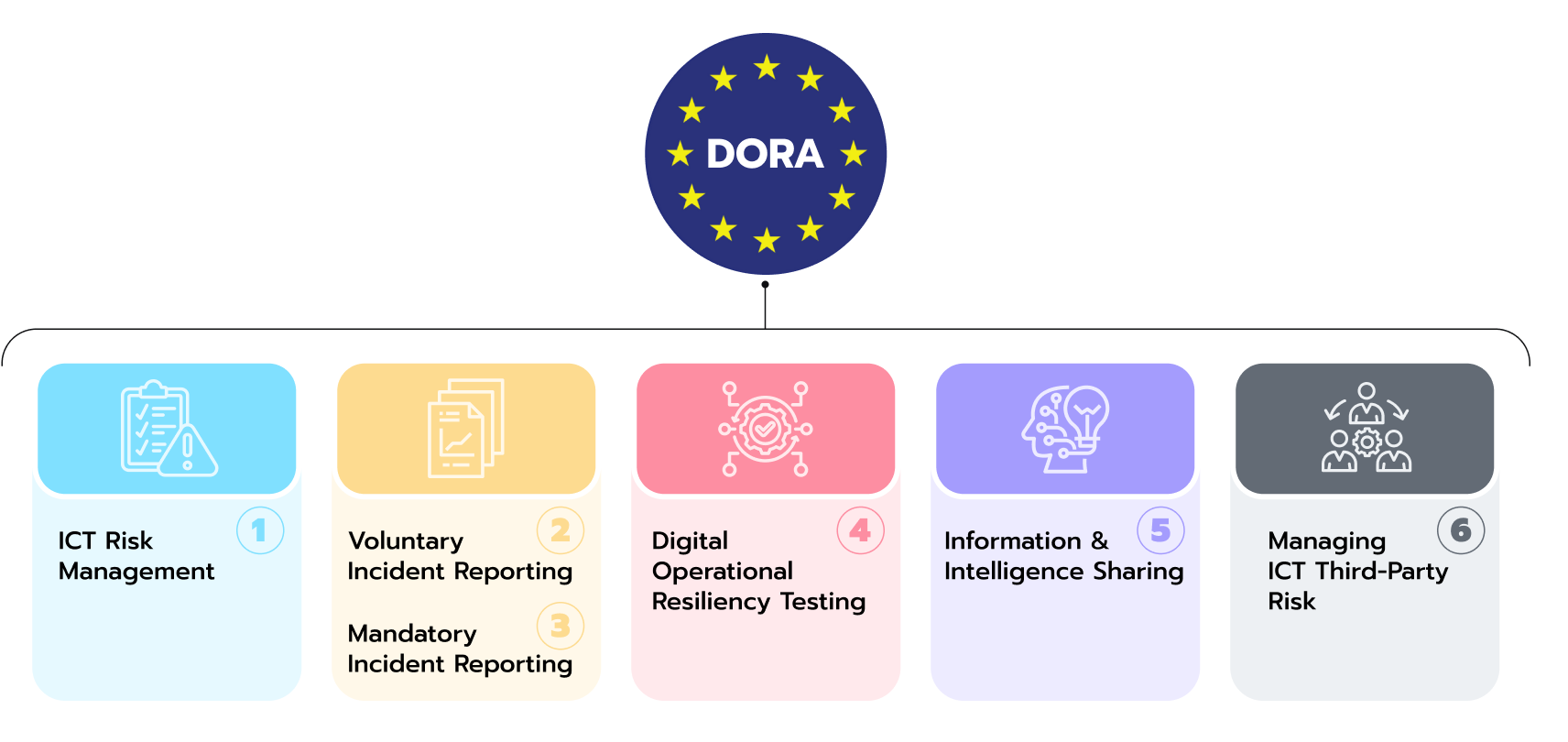 Fig 2. DORA requirements.
Fig 2. DORA requirements.
API-based banking and open banking
Open banking allows financial services and products to be exchanged securely between banks, fintechs, and third parties through APIs. This levels the playing field and fosters innovation.
The use of APIs will increase to improve connectivity between banking systems. Banks will continue opening up APIs and collaborating with fintechs to co-create solutions. Customers will also benefit from personalized products.
- Open banking allows financial information and services to be shared through APIs between banks, financial technology companies, and third-party developers.
- It enables the creation of open ecosystems where banking functions can be exchanged seamlessly between multiple parties.
- Banks are opening up APIs to allow other companies to develop applications and services around the bank’s data and systems.
- This API connectivity facilitates seamless integration between banking systems and third-party apps. Customers can authorize financial data to be accessed.
- It allows fintechs to build innovative banking products and services by leveraging the infrastructure of banks through APIs.
- Banks can also benefit by reaching more customers through third-party apps that use the bank’s APIs to provide services.
- Open banking improves the range, quality and convenience of banking services available to customers.
- API-based banking allows faster product development and time-to-market through collaboration between banks and fintechs.
- Banks will increasingly adopt microservices architecture and create more fine-grained APIs for specific banking functions.
- Standardization of open banking APIs through initiatives like Open Banking UK promotes seamless interoperability.
It should be noted that the introduction of PSD3 (Payment Services Directive 3) in the EU is prompting significant changes for banks and the open banking landscape. This is what banks are doing to prepare themselves for the upcoming regulation:
- Strengthening security: PSD3 mandates stricter authentication measures for online payments, requiring stronger customer authentication (SCA) to combat fraud. To comply, banks are implementing new technologies like 3D Secure 2.0 and biometrics.
- Enhancing data protection efforts: PSD3 emphasizes stricter data protection regulations, requiring banks to be more transparent and obtain explicit consent from customers before sharing their data with third-party providers (TPPs). Banks are reviewing and updating their data governance practices to ensure compliance.
- Openness to competition: PSD3 aims to level the playing field for TPPs, granting them broader access to customer payment data through Open Banking APIs. Banks are building and enhancing their APIs to meet these requirements and facilitate secure data sharing.
- Operational adjustments: PSD3 introduces new reporting requirements and mandates collaboration among payment service providers (PSPs) for fraud prevention. Banks are adapting their internal processes and infrastructure to comply with these regulations.
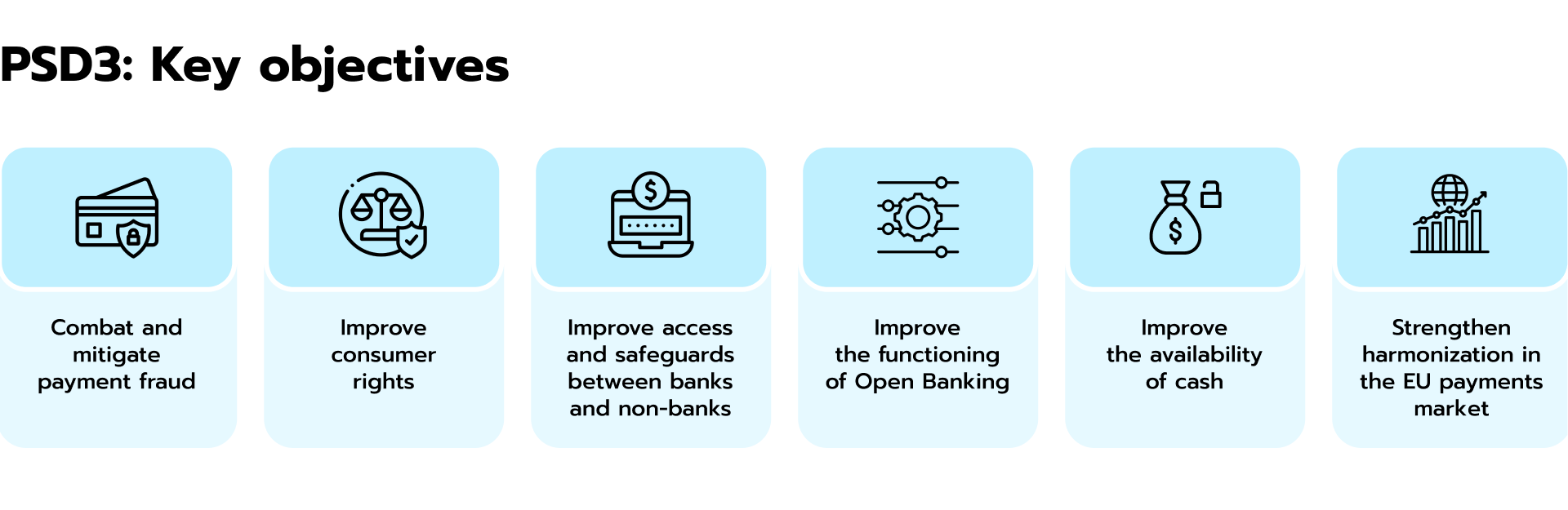 Fig 3. PSD3 objectives
Fig 3. PSD3 objectives
Impact on Open Banking
- Increased adoption: PSD3’s emphasis on open banking is expected to drive wider adoption of TPP services, potentially leading to more innovative financial products and competition in the market.
- Improved security and transparency: Stronger authentication and data protection measures mandated by PSD3 will benefit open banking by enhancing the overall security and transparency of data sharing within the ecosystem.
- Standardized access: PSD3 aims to harmonize open banking regulations across the EU, leading to a more standardized approach for TPPs to access customer data, potentially simplifying their operations.
- Potential challenges: Banks may face challenges in building robust APIs, complying with data protection requirements, and managing the potential increase in data access requests from TPPs.
Cloud computing
Cloud technology is poised to continue its role as a catalyst for innovation in the banking sector. By embracing cloud-based solutions, banks can minimize reliance on physical infrastructure, leading to cost savings and quicker rollout of new features to meet evolving customer needs. This is especially crucial as regulations surrounding cloud adoption become more favorable, allowing banks to turn their attention towards innovating their core processes and systems on the cloud.
Areas that will see increased cloud adoption include data management, AI, analytics, digital payments, and cybersecurity systems. Cloud will enable banks to innovate rapidly.
- Cloud provides banks with an agile infrastructure that can be scaled up or down based on needs. This enables faster deployment of new capabilities.
- Banking workloads, such as risk modeling, data analytics, mobile banking, payments, etc., are increasingly shifting to the cloud from on-premises data centers.
- Cloud enables real-time data processing that allows banks to derive insights faster and improve decision-making.
- Banks are adopting public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid models, depending on regulatory requirements and workload needs.
- Cloud services provide banks with access to the latest technologies, such as AI machine learning.
- Cloud-based software helps minimize upfront capital expenditure and converts costs into operating expenditures for banks.
- Cloud facilitates collaboration between banks and external partners like fintech firms through seamless data sharing.
- Banks are using the cloud to develop customer-facing applications faster and improve customer experience.
- Security and governance remain key considerations as banks migrate sensitive data and workloads to the cloud.
- Multi-cloud strategies are emerging as banks use different cloud platforms based on costs, capabilities, and avoidance of vendor lock-in.
Customer experience technologies
Banks will harness technologies like chatbots, visualization, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) to transform customer experience. Chatbots are already enhancing customer service. Visualization through data visualization tools simplifies complex data. AR and VR can be used to bring banking products and services to life interactively. These technologies provide immersive, personalized experiences that build trust and long-term customer relationships.
- Intelligent data visualization dashboards simplify complex data for customers to understand their finances, transactions, investments, etc. more easily.
- Augmented reality and virtual reality are being used by banks to provide immersive experiences like virtual branch tours, interactive financial planning, etc.
- Banks are implementing biometrics like facial recognition, voice recognition, and fingerprint scanning to make customer onboarding and transactions easier and more secure.
- Advanced data analytics and AI enable banks to gain customer insights and provide hyper-personalized recommendations and offers.
- Sentiment analysis based on machine learning algorithms helps banks gauge customer feedback shared on channels like social media and review sites.
- Omnichannel integration across channels like mobile, web, call center, ATM, and branches provides customers with a seamless experience.
- Location-based services leverage data like footfall and GPS to push personalized notifications to customers near branches with relevant offers.
- Video KYC using computer vision technology enables remote, real-time customer onboarding by banks through video analysis.
Learn more about how we elevated automation performance testing for a global finance leader. Success story
Cybersecurity and fraud management
Banks hold sensitive customer data, making them a target for cyberattacks. Advancements in cybersecurity and fraud management will remain a priority. Banks are already using AI to detect suspicious account activity and block fraudulent transactions in real time. Biometrics are also on the rise for identity verification. Encryption, cyber threat monitoring, perimeter defense, and vulnerability testing will see increased investment.
- The adoption of AI and machine learning for real-time detection of fraud, suspicious transactions, malware attacks, unauthorized access attempts, etc., enables prompt response to modern cyberthreats.
- Behavioral biometrics, such as keystroke analysis and gestures, are used to constantly validate user identity and prevent fraudulent account access.
- Implementation of robust data encryption, tokenization and masking to protect sensitive customer data across banking systems and processes.
- Increased investment in cybersecurity talent and 24/7 security operations centers for preventing, detecting, and responding to cyber threats.
- Adoption of multi-factor authentication mechanisms like one-time passwords, fingerprints, iris scans, etc., to reinforce account security.
- Conducting predictive data analytics to identify irregular transactional patterns and prevent future frauds or cyberattacks.
- Moving towards zero-trust models and software-defined perimeters to isolate access and minimize internal threats.
- Increased collaboration between banks to share intelligence on cyber threats and fraud typologies through forums like FS-ISAC.
- Annual cybersecurity audits, attack simulations, vulnerability testing, and risk assessments to identify and address gaps proactively.
- Adopting frameworks like ISO 27001 and NIST Cybersecurity Framework to align with global information security standards.
Digital banking and payments
The use of digital channels like mobile apps for banking will continue to grow. Peer-to-peer payment options and digital wallets are also gaining prominence.
Banks are collaborating with fintech payment companies to enable real-time digital payments globally. Cryptocurrency adoption is also rising. Banks are working to improve their payment infrastructure to match these trends.
- Mobile banking apps have become the primary digital interface between banks and customers for activities like account management, transfers, deposits, etc.
- Digital wallets like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal are being integrated into their mobile apps by banks to enable contactless payments.
- Adoption of payment technologies like NFC, QR codes, and mobile point-of-sale allows faster checkout and peer-to-peer transfers.
- Real-time payments through faster settlement systems like TCH RTP and FedNow enable instant fund transfers between bank accounts 24/7.
- Partnerships between banks and fintechs are increasing to provide enhanced digital payment experiences to customers.
- Banks are modernizing their payment systems and infrastructure to support real-time digital transactions globally.
- Open banking and API integration are enabling more embedded finance options for customers directly via merchant apps.
- Authentication technologies like biometrics, behavioral analytics, and AI are improving payment security while maintaining ease of use.
Summing up
The banking industry is at the cusp of a technological revolution. Banks are aggressively adopting automation, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and advanced data analytics. These technologies are enabling them to reinvent customer experiences, streamline operations, manage risks better, and offer innovative new services.
In addition to these advancements, the industry is also being shaped by new regulations like DORA (Data Act), PSD3 (Revised Payment Services Directive), and the ongoing adoption of GenAI. These regulations aim to ensure responsible data use, open banking practices, and ethical implementation of AI in finance. Banks that can adapt their technology adoption strategies to comply with these regulations will be well-positioned for success in the evolving landscape.
By harnessing such emerging technologies holistically, banks can build the next generation of intelligent, insights-driven, and customer-centric digital banking. Technology, coupled with regulatory compliance, is at the core of the transformation that will help incumbent banks survive the fintech revolution. This tech-first mindset across automation, AI, blockchain, cloud, analytics, and responsible data practices will define the future of banking and help banks stay competitive now and in the years ahead.
For those prepared to adopt these emerging trends, Avenga stands ready to facilitate and streamline your journey into technological innovation. Reach out to us, taking a decisive step towards a digitally-driven financial future.

 Fig 1. GenAI in banking.
Fig 1. GenAI in banking. Fig 2. DORA requirements.
Fig 2. DORA requirements. Fig 3. PSD3 objectives
Fig 3. PSD3 objectives