AI’s omnipresence in today’s and future telecom industry explained
Learn how AI is transforming the telecom industry and dive into its power to enhance customer experience in 2025 and beyond.
Peeling back the layers of data science in healthcare.
Healthcare has been a data repository for quite some time. Electronic Healthcare Records (EHRs), patient summaries, clinical test results, medical imaging, and insurance claims represent just a fraction of the diverse and extensive data sources that have been generated at an unprecedented rate. As a 2023 Deloitte report highlights, the life sciences and healthcare industries account for 30% of the world’s data. The implementation of data science methods in this context serves a dual purpose: to help extract new knowledge and to transform healthcare delivery, thus creating new opportunities for better patient outcomes. In this article, we will discern the nuanced mechanisms through which data science is reshaping the healthcare industry, from increasing the rate of accurate first-time-right diagnoses to curbing the incidence of lifestyle-related diseases.
Data science combines multiple disciplines and techniques that allow healthcare actors to discover areas where progress can be made. While primarily anchored in methods such as big data analytics, data mining, Artificial Intelligence (AI), statistics, advanced Machine Learning, computer vision, and semantic reasoning, its scope isn’t confined to these alone. Such a wide array of data science techniques allows healthcare institutions to break down data silos and refine decision-making. When it comes to healthcare data analytics, there are four primary research perspectives available to data scientists:
One of the main reasons data science offers a bright promise to healthcare is the unprecedented data deluge that has engulfed the healthcare sector. With the rapid digitization of healthcare systems, an immense volume of data is generated daily. EHRs, clinical trial data, health insurance claims, wearable devices, genetic and genomic data, medical imaging, and even patient-generated data from sources like mobile health applications and social media interactions contribute to this vast pool of information (see Fig 1.). According to the global investment bank RBC Capital Markets, the annual growth rate of healthcare data is set to achieve a 36% increase by 2025, outpacing other sectors such as manufacturing, financial services, as well as media and entertainment.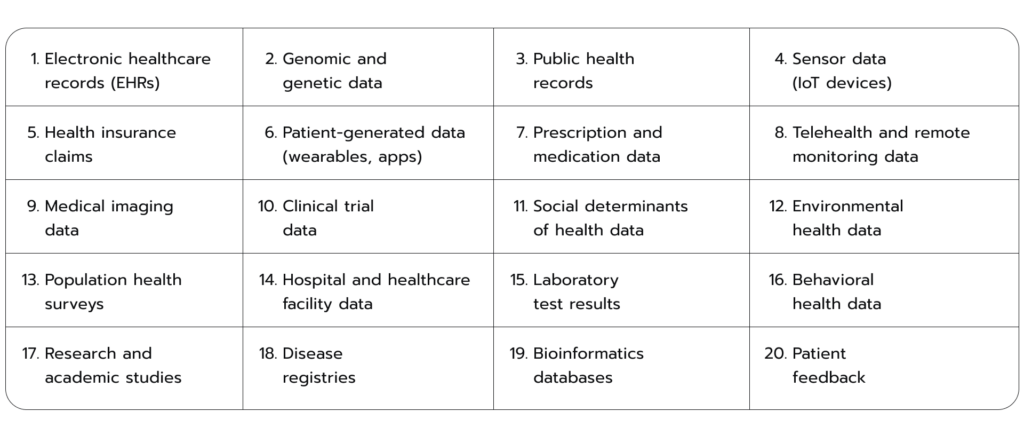 Figure 1. A list of data sources in the healthcare industry
Figure 1. A list of data sources in the healthcare industry
This data tsunami can be seen both as a challenge and an opportunity. On the one hand, researchers are often confronted with questions of how to access or gather representative data with high-quality annotations. Moreover, data often comes in an unstructured form from different sources, creating a challenge of interoperability. Privacy and security pose other concerns for those dealing with large data volumes, especially when it comes to vulnerable patient health data. These nuances are just a drop in the ocean of healthcare’s complex data science landscape.
On the other hand, the sheer volume and diversity of data offer the potential for significant discoveries and improvements in patient care, research, and healthcare systems. This wealth of data provides researchers with an extensive foundation on which to base their investigations of the human body. It allows for the exploration of advanced strategies of drug development, the identification of novel biomarkers, and the exploration of new approaches to clinical trials. Moreover, healthcare administrators and policymakers can leverage data-driven insights so as to make informed decisions about resource allocation, infrastructure development, and policy planning.
What’s more, AI, with its ability to analyze complex patterns, has become a linchpin in healthcare data analysis in recent years. Particularly adept at handling rich data types, such as genetic sequences, medical images, and electronic health records, it can process these multifaceted datasets swiftly and accurately. In a recent Nature survey of more than 1,600 researchers, the majority of respondents admit that AI offers faster ways to process data, accelerates computations, and saves an individual’s time and/or money. Meanwhile, the number of research papers mentioning AI or Machine Learning concepts in their titles or abstracts has increased up to 5% in life sciences and healthcare from 1983 to 2023.
Learn how Avenga created a HIPAA-compliant patient engagement platform that enables hundreds of medical teams across the US to communicate with tens of thousands of their patients. Success story
From propelling precision medicine to advancing public health, data science in healthcare is found in applications across the various healthcare segments and serves diverse purposes. Let’s delve into the implementations of data science tools in the industry:
For example, healthcare providers can achieve greater operational efficiency through process mining, which implies the analysis of event logs to grasp and optimize processes. In healthcare, this translates into evaluating the sequences of activities that occur during patient care. Following the journey from admission to discharge, administrators can pinpoint delays and continuously monitor performance across various departments.
One noteworthy example of how healthcare facilities can leverage data analytics for green performance is the concept of the Big Data Analytics Capability (BDAC). Researchers emphasize that BDAC can enhance information sharing and streamline internal communication, enabling healthcare organizations to adopt more environmentally friendly practices. In addition, through precise demand forecasting and efficient logistics, BDAC can minimize unnecessary resource consumption.
Despite being in its earliest days, data science holds the potential to become a cornerstone in the emergence of a value-based care model that places the focus squarely on patient outcomes and the efficient use of resources. Here are some of the key benefits it can bring to the healthcare industry:
Today, healthcare professionals are increasingly equipped with a powerful toolset to navigate the complexities of patient care, administrative efficiency, and public health management intricacies. In the coming years, data-driven decision-making will likely extend its influence beyond clinical practices to shape healthcare policies and public health initiatives. Governments and healthcare institutions will leverage data analytics to formulate strategies for disease prevention, healthcare resource planning, and the development of innovative treatments.
This intersection of data science and healthcare is not merely a trend. It represents a fundamental shift in how we are approaching medical challenges. Data science, embedded with advanced analytics tools, Machine Learning algorithms, and AI technology, acts as a guiding force for extracting relevant insights from this wealth of information. But, although it offers a bright prospect for the future, cohesive, meaningful, and impactful digitalization is still in its early stages. The application of new instruments requires a gradual transition towards digital healthcare systems where the patient takes center stage. This may be the way for us to unlock the full potential of data, ushering in a phase where the healthcare industry represents not only reactive and curative treatment, but stands as a truly personalized, preventive, and participatory experience.
Avenga helps healthcare companies discover actionable data-driven insights at the right time with the right toolkit. Learn more about our expertise in the domain: contact us.
* US and Canada, exceptions apply
Ready to innovate your business?
We are! Let’s kick-off our journey to success!