Major transportation industry trends in 2026

December 9, 2025 17 min read
Picture a highway where self-driving trucks zoom past, drones buzz overhead dropping off packages, and electric cars glide by without a sound. That’s the future of transportation technology, and it’s speeding toward us faster than you might expect! The transportation industry is undergoing rapid change, driven by new technologies, shifting customer demands, and emerging regulations that are transforming how goods and people are moved.
In this article, we’re diving into the exciting forces set to shape our roads, railways, skies, and seas over the next few years. We’ll unpack the innovations driving transportation trends, tackle the challenges plaguing the supply chain, and take a look ahead at what’s next for the sector.
Stick with us to discover the key factors steering the transportation industry toward 2026 and beyond.
Key takeaways
- Technology is reshaping the future of transportation technology, with AI, autonomous vehicles, IoT, and digital twins improving operations with safety, efficiency, and intelligence.
- Electrification and sustainability are becoming indispensable and non-negotiable in transport with EV adoption, alternative fuels, and green logistics transforming industry trends and developments in 2026.
- Data and digital transformations are now central benefits, providing instantaneous decision support, predictive maintenance, and clearer supply chain visibility.
- Climate resilience and changing regulations will change the face of global networks and organizational networks by modifying and diversifying hindering routes and applying active transport strategies to ensure long-term operational stability.
Trend #1. Embracing technological advancements
Technology plays a central role in modernizing the transportation industry, enabling companies to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. Businesses are increasingly investing in digital tools such as artificial intelligence (AI), autonomous vehicles, and the Internet of Things (IoT), which are now becoming standard across the sector.
Autonomous vehicles and advanced telematics
Autonomous vehicles are pushing the boundaries of innovation in the transportation sector. Leading car manufacturers and technology companies are developing self-driving cars and trucks that leverage sensor technology and AI to navigate roads autonomously. These vehicles aim to minimize human error, improve safety, and optimize fuel efficiency. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), self-driving cars have the potential to reduce traffic accidents by as much as 90%. The global autonomous vehicle market is projected to reach $65 billion by 2027, reflecting significant investments from industry leaders like Tesla and Waymo.
These advancements promise not only safer roads but also reduced fuel consumption and optimized route planning. The fact that the telematics market experiences a CAGR in the U.S. alone is a significant piece of the puzzle (see Graph 1).
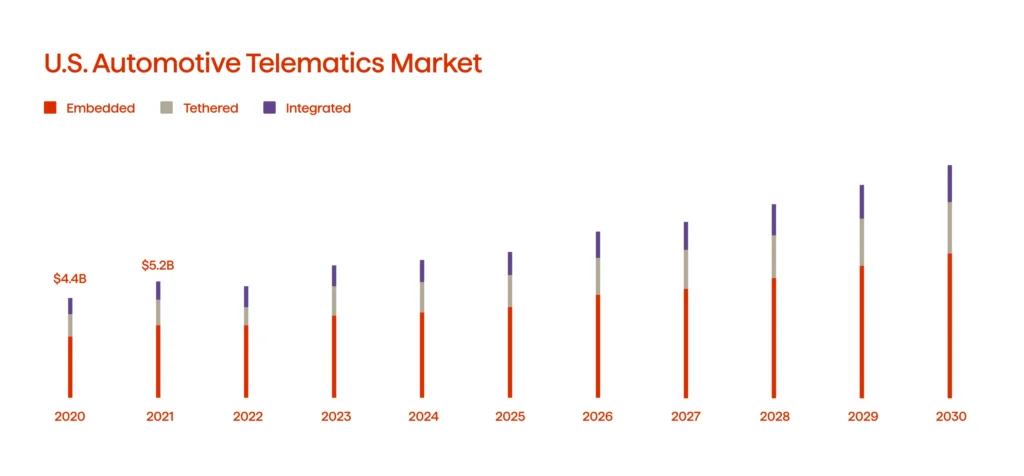
Telematics has emerged as an indispensable tool for fleet management. By providing real-time tracking, companies can monitor vehicle locations, performance metrics, and driver behavior, including speed and fuel consumption. Sensors collect this data, which is then analyzed using advanced analytics to predict maintenance needs. This proactive approach reduces downtime and ensures smoother fleet operations. A study by Verizon Connect shows that telematics can decrease fuel consumption by up to 15% and maintenance costs by 14%.
Integration of blockchain and IoT
Blockchain technology is being adopted to enhance transparency in the supply chain. By providing an immutable ledger of transactions, blockchain increases trust among stakeholders. It helps verify the movement of goods and minimizes the risk of fraud. This application is critical in sectors such as freight transportation and last-mile deliveries. Companies like Maersk are already implementing blockchain solutions to streamline their supply chains.
Next, along with blockchain, there is the Internet of Things (IoT). The IoT in transportation market is experiencing one of the fastest growth rates in the entire industry (see Graph 2).
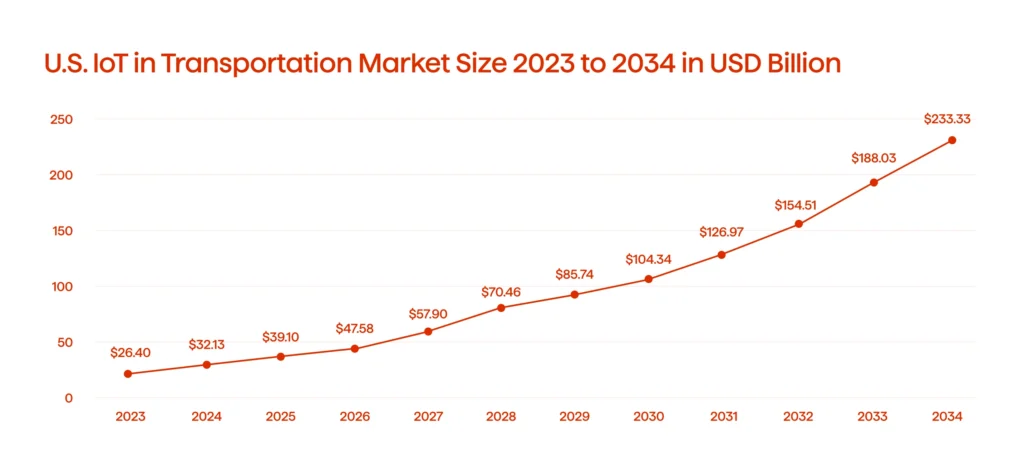
These advancements are not merely transportation trends. They represent evidence-based solutions grounded in facts and innovation. By integrating AI, autonomous vehicles, telematics, blockchain, and IoT, the transportation industry is poised for a more efficient, safe, and transparent future. The statistics and examples provided underscore the transformative impact of these technologies, supported by reputable sources.
At Avenga, we specialize in delivering cutting-edge asset tracking and management solutions that empower logistics and transportation companies
Trend #2. Electrification and sustainability
The push for sustainability is now a leading focus in the transportation industry. Electric vehicles (EVs) are spearheading this movement. The global transition away from fossil fuels is accelerating. Both governments and consumers are calling for cleaner, zero-emission options.
Growth of electric vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles are gaining popularity (see Graph 3). Car manufacturers and fleet operators are investing heavily in EVs to comply with increasingly stringent emission regulations. Advances in battery technology are making EVs more efficient and affordable. Charging infrastructure is rapidly expanding to meet this demand. As more drivers adopt EVs, cities will benefit from cleaner air and quieter streets. According to a report by BloombergNEF, electric vehicles are projected to account for 58% of global passenger car sales by 2040, driven by advancements in battery technology and supportive government policies.
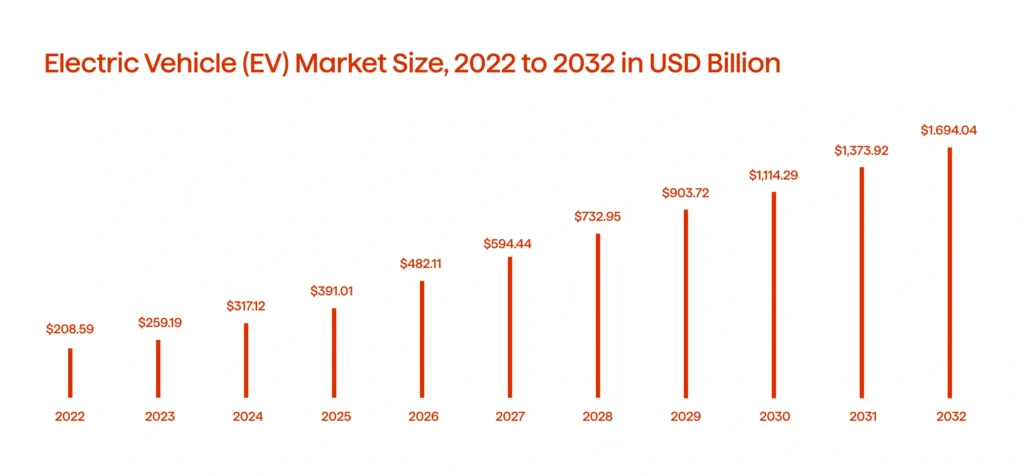
Commercial fleets are also shifting toward electrification. Companies are replacing diesel trucks with electric alternatives. This change not only cuts emissions but also reduces operational expenses. Improved battery life and faster charging times are speeding up the transition. Many industry experts predict that electric commercial vehicles will become the standard by 2026.
Sustainable practices across the supply chain
Sustainability efforts extend beyond vehicle emissions. They encompass the entire supply chain. Companies are rethinking logistics operations to minimize waste. From optimizing routes to using eco-friendly packaging, every step is being evaluated for its environmental impact. These initiatives help reduce the overall carbon footprint of the transportation industry, as per 2026 trends.
The adoption of alternative fuels, including hydrogen and biofuels, is also on the rise. These fuels offer viable solutions to reduce dependence on traditional sources. Through ongoing research and development, new fuel technologies are expected to play a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Trend #3. Innovations in last-mile delivery
Last-mile delivery remains one of the most challenging components of logistics (see Graph 4). It’s the final step in delivering goods to customers, and it’s both expensive and complex. Fortunately, new technology is tackling these issues directly.
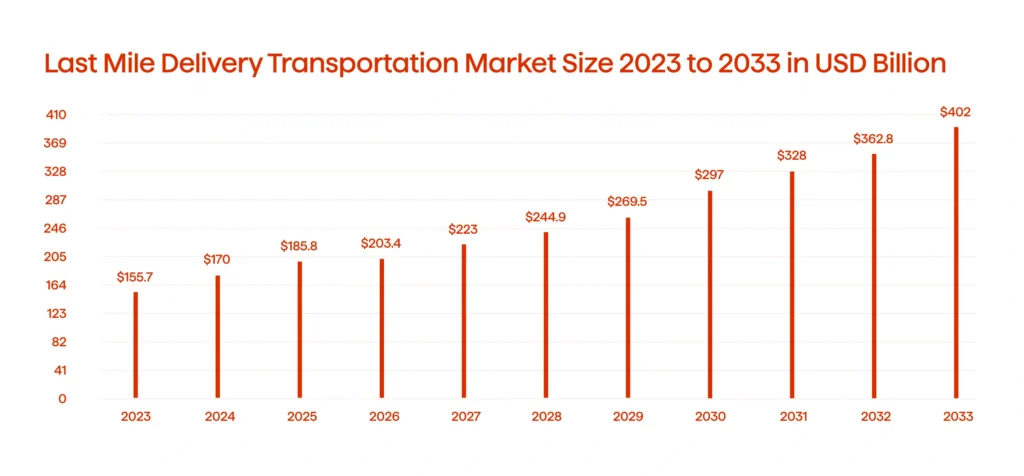
Efficiency gains in last-mile operations
The rise of online shopping has made last-mile delivery a significant challenge. Delivering a package right to a customer’s door can account for up to 50% of the total shipping cost. To address this, companies are experimenting with automation and crowdsourcing. For example, they’re testing self-driving delivery vehicles and drones to enhance efficiency. These tools enable efficient navigation of cities and reduce delivery times.
Data analytics helps improve last-mile routes. Companies analyze live traffic, weather, and delivery schedules to find the fastest paths. This cuts fuel use and ensures packages arrive on time. As a result, customers are more satisfied.
The role of crowdsourcing and micro-logistics
Crowdsourcing is another clever solution for last-mile delivery. Platforms connect freelance drivers with delivery jobs, and this approach is growing popular. It allows companies to adjust their operations according to their level of activity. In crowded city areas, micro-logistics, such as using bikes, electric scooters, or walking couriers, can be faster and more cost-effective.
These new ideas are part of larger trends in transportation and logistics that are reshaping the industry. They help companies remain flexible and meet customer demands in a rapidly evolving market. By adopting these technologies, transportation companies can lower costs and reduce their environmental footprint.
Trend #4. Digital transformation and data-driven decision making
Data is the new fuel driving the transportation industry. The digital revolution has transformed the way companies operate. Fleets, warehouses, and logistics networks now produce vast amounts of data. This data enables companies to make more informed decisions.
Real-time tracking and predictive analytics
Real-time tracking systems deliver a steady flow of information. Technologies such as GPS and sensors track vehicle locations, fuel levels, and driver performance. This data powers predictive analytics tools, which predict maintenance problems before they happen. Companies can then schedule repairs in advance, reducing downtime and costs. A 2024 study found that real-time tracking and data analytics can reduce delivery delays by 30% and improve route planning by 25%.
Predictive analytics also improves route optimization. By analyzing past data and current conditions, companies can determine the fastest and most fuel-efficient routes. This lowers costs and prevents delays. For example, algorithms can suggest new routes when traffic jams or road closures occur. A 2023 report indicates that predictive analytics can reduce transportation maintenance costs by up to 20% and increase fleet efficiency by 15%.
Enhancing supply chain visibility
Data-driven decision-making brings transparency to the supply chain. Real-time data lets companies track goods from the manufacturer to the consumer. This visibility enhances teamwork among supply chain partners, identifies bottlenecks, and streamlines operations, from warehouse management to last-mile delivery.
Many companies are investing in transportation management systems (TMS). These systems combine data from telematics, sensors, and customer feedback into one dashboard. This setup enables fast and informed decisions. As the need for efficient and reliable logistics grows, these systems are becoming vital.
Trend #5. Growth in mobility as a service (MaaS)
Mobility as a Service (MaaS) has been greatly reshaping urban transportation (see Graph 5). MaaS integrates various modes of transportation into a single, accessible service. It connects public transit, ride-hailing, bike-sharing, and car rentals, allowing users to plan, book, and pay for their entire trip in just a few steps.
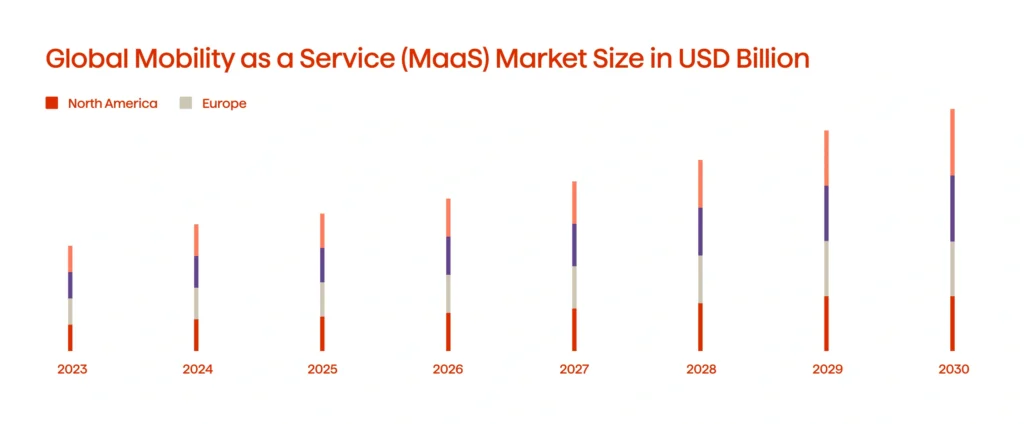
Integration of multimodal transportation
MaaS simplifies transportation by linking various modes of transportation. With real-time data on schedules, travel times, and costs, people can pick the best option for their journey. This seamless integration enhances convenience and reduces traffic congestion. For example, a study shows that MaaS could reduce private car use in cities by up to 30%, easing congestion and making streets less crowded.
MaaS platforms not only improve convenience but also reduce congestion. By offering alternatives to private vehicle ownership, these platforms contribute to lower emissions and a more sustainable urban environment. This innovation is a crucial component of current transportation trends. As cities become more connected, MaaS will play a significant role in shaping how people move around.
The economic and environmental benefits of MaaS
Mobility as a Service (MaaS) is transforming the way we move in cities, offering a smarter and more connected way to travel. It’s a game-changer for both consumers and businesses, with benefits that also extend to the environment.
- Flexibility for users. MaaS offers a range of options, including public transit, bike-sharing, and ride-hailing, allowing users to choose the best option for each trip, with no car ownership required.
- Cost savings. Users avoid expenses such as car maintenance and parking, while businesses lower costs by optimizing services rather than managing large fleets.
- Reduced traffic. Fewer private cars on the road ease congestion, cutting travel times and making cities less crowded.
- Lower emissions. Cities adopting MaaS could see a 20% reduction in transportation-related carbon emissions by 2030, thereby improving air quality.
- Enhanced livability. Less pollution and traffic make urban areas cleaner, quieter, and more pleasant places to live.
As cities grow smarter, MaaS is poised to shape transportation trends in 2026 and beyond. It’s more than just travel — it’s a step toward efficient, cleaner, and better urban living for all. This approach is one of the key transportation industry trends for 2026 that will shape the future.
Trend #6. Workforce challenges and innovations
The transportation industry is facing serious workforce challenges. There aren’t enough drivers, and many current drivers are getting older. In fact, the U.S. alone has a shortage of about 80,000 truck drivers, according to the American Trucking Associations. This shortage, combined with an aging workforce, exacerbates the problem. But new technology is helping to address these issues.
Addressing the driver shortage
Transportation companies are struggling to find qualified drivers. The job is physically demanding, and as drivers age, it becomes harder to keep up. To address this, companies are exploring the use of automation and self-driving vehicles. While fully self-driving trucks are not yet available, partial automation is already making a difference. Systems like Advanced Driver-Assistance (ADAS) help drivers stay alert and drive more safely by reducing fatigue.
Companies are also updating their training programs to attract younger workers. They’re using simulators and online tools to teach new drivers. These methods allow people to practice without the risks associated with real roads, helping to build a stronger, younger workforce.
Shifts in fleet management
Technology is also transforming how fleets are managed. Digital tools simplify scheduling, performance tracking, and route planning. Sensors provide real-time data on fuel consumption, driver behavior, and vehicle health, all from a single central system.
These innovations save money. Companies spend less on truck repairs and fuel. They also improve safety by addressing problems before they escalate. Embracing this technology is a significant trend shaping the future of transportation technology and logistics.
Trend #7. Infrastructure investments and future supply chain innovations
Robust infrastructure is critical for the evolution of the transportation sector. Investments in roads, bridges, railways, and digital networks support the new wave of technological advancements. As urban areas continue to grow, the demand for improved infrastructure will only increase.
Modernizing transportation infrastructure
Governments are prioritizing infrastructure upgrades. These efforts include building new highways, modernizing rail systems, and expanding public transit options. The goal is to create a resilient and efficient transportation network. In addition, there is a focus on integrating innovative technologies into infrastructure. Sensors, cameras, and connected devices are being installed to monitor traffic flows and optimize transit routes in real time.
Investments in digital infrastructure are equally important. High-speed communication networks support real-time data exchange among vehicles, traffic management systems, and logistics platforms. These networks enable the advanced telematics and predictive analytics discussed earlier. Improved infrastructure not only supports current operations but also paves the way for future innovations in the transportation industry, as per 2026 trends.
Enhancing supply chain resilience
Supply chain resilience is a major concern in today’s global economy. Disruptions—whether due to natural disasters, geopolitical issues, or pandemics—can have a significant impact on the flow of goods. Transportation companies are responding by diversifying their supply chains and investing in risk management strategies to mitigate potential disruptions.
Innovations such as blockchain technology and real-time tracking are making supply chains more transparent and efficient. This increased visibility allows companies to respond quickly to disruptions. They can reroute shipments, adjust inventory levels, and maintain continuity of service. Such measures are crucial in ensuring that the supply chain remains robust even in the face of unexpected challenges.
Trend #8. Regulatory and economic influences
Government policies and economic factors play a critical role in shaping the transportation landscape. Regulatory measures affect everything from vehicle emissions to safety standards. At the same time, financial factors such as fuel prices and trade policies impact operational costs.
Environmental regulations and emission standards
Stricter environmental regulations are being implemented worldwide. Governments are pushing for lower emissions and greener practices. For example, new regulations mandate the transition to zero-emission vehicles for heavy-duty fleets. These policies aim to reduce the environmental impact of the transportation sector. Companies that adapt quickly will gain a competitive advantage in a market that is increasingly focused on sustainability.
Economic pressures and fuel prices
Fuel prices continue to be a significant concern for transportation companies. Fluctuations in oil and gas prices directly affect operational costs (see Graph 7). Companies are actively seeking ways to reduce fuel consumption through better route planning and more efficient vehicles. The adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles is one such strategy. As fuel prices stabilize or drop, companies can pass on savings to consumers while maintaining profit margins.
Trend #9: Climate resilience and extreme weather adaptation
Climate-driven disruptions are now one of the most significant hazards to global transport networks. From flooded roadways to heat-warped rail lines and storm-shuttered ports, extreme weather conditions are changing how goods and people move across the globe. The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) projects that the damage to infrastructure caused by climate-related events exceeded $600 billion in the last five years.
Growing climate impacts on transportation networks
Transportation systems are not designed to withstand the level of climate volatility we are currently experiencing. Heat waves can cause rail operators to reduce speeds or shut down sections of track because of potential steel expansion. Territorial rain and flooding will temporarily shut down major highways, resulting in shipment delays of 2-3 days.
Ports such as Los Angeles, Rotterdam, and Shanghai have begun to report significant slowdowns in operations due to storm surges, wind events, or coastal flooding.
Atmospheric effects are worse for aviation. According to the latest research on flight route operational conditions, severe turbulence has increased by 55% across major flight corridors, causing airlines to reroute and add fuel buffers.
How companies are adapting
Transportation and logistics businesses are employing tools and technologies that strengthen the resilience of their networks:
- AI-driven climate analytics. Logistics platforms now leverage real-time weather intelligence to reroute freight dynamically, adjust departure times, or change modes of transport altogether. For instance, under current conditions, DHL leverages a predictive weather service to modify freight ahead of an approaching storm.
- Climate-resilient infrastructure. Infrastructure upgrades and changes are already underway at ports, including the construction of container yards, protective structures such as sea walls, and enhanced drainage systems, to accommodate higher water levels. Rail companies operating particularly in the EU are upgrading from old rails to heat-resistant steel to prevent bending due to extreme heat.
- Alternate network strategies. Shippers are reshaping their networks by diversifying routes to avoid high-risk corridors, setting up micro-fulfillment centers to minimize their exposure to weather events, and adopting multimodal networks when necessary.
- Insurance company-driven adaptation. As insurance companies have adjusted their underwriting practices and begun to enhance underwriting requirements, many logistics companies are conducting climate-risk audits and implementing resilience standards to reduce insurance costs and maintain compliance.
As extreme weather events are reported to become more disruptive and more frequent, climate resilience will evolve from a focus on operational optimization to a central strategic imperative. Firms that can incorporate climate intelligence, redesign infrastructure, and establish flexible routing efforts will fare better than companies reacting to disruptions after they occur.
FAQ
Final words
The journey ahead for the transportation industry is both challenging and full of promise. The changes we are witnessing today, from autonomous vehicles to sustainable logistics, are setting the stage for a future where efficiency and sustainability are inextricably linked. The focus on real-time data, digital transformation, and integrated mobility solutions will drive the sector forward. By embracing these changes, transportation companies can optimize operations, reduce costs, and lower emissions.
The future of the transportation industry is clear. The combination of advanced technologies, regulatory support, and shifting consumer expectations will pave the way for new trends in transportation that redefine the way we move. As we look to 2026 and beyond, these changes are not just innovations on paper—they are already taking shape on our roads, rails, and skies.
Want to learn more about the strategic transportation technology trends for 2026 and beyond?Contact Avenga, your trusted expert in transportation software development services.