Telecom industry trends 2026: Prepare for the future

February 10, 2026 11 min read
Telecom stocks performed well in 2024, rising about 11% over the past year. Still, that’s not even close to the S&P 500’s 25% jump or the NASDAQ’s 30% surge. It’s the same old story heading into 2025: the market chases excitement, and steady demand just isn’t enough to make telecom feel like a true growth sector anymore.
As a result of the growing demand for seamless customer experiences, continued investment in network infrastructure, and the rapid proliferation of software-based service delivery models, the telecommunications industry is facing increased scrutiny across all areas of operation. AI will provide telecom companies with a competitive advantage. It helps automate the management of future networks, improves their operational resiliency, and leverages their operating data to inform meaningful business decisions. This article highlights the key telecom technology trends driving organisations to differentiate themselves throughout 2026 and beyond.
Key takeaways on the telecommunications industry trends
- These days, network management is increasingly centered on AI. Telecoms utilize it to expedite the rollout of updates across their 5G networks, enhance performance, and automate repairs.
- Cybersecurity is no longer limited to the IT department. These days, it’s crucial for businesses to preserve relationships, revenue, and client trust.
- With shorter deployment periods than standard fiber constructions, edge computing, private 5G, and FWA are enabling new services for enterprises and increasing coverage.
- Open RAN and BSS/OSS microservices are revolutionizing the way operators operate. They make it easier to work with different vendors, avoid getting locked in, and keep up with what the 6G era demands.
Telecom industry trends 2026: what’s driving change
Now, without further ado, let’s review key global telecom trends shaping the industry.
Network automation and AI-driven operations
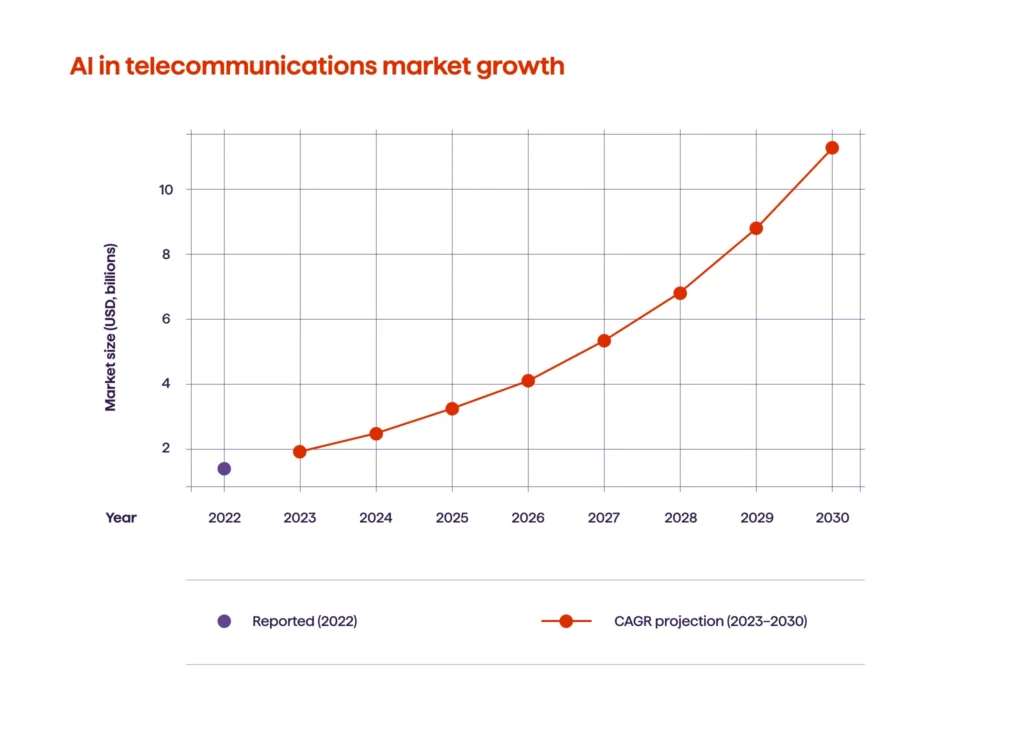
Network automation and AI-driven operations are enabling telecom networks to operate largely autonomously. With 5G, everything’s getting more complicated—think more cells, more slices, more edge nodes. Operators must keep up by rolling out services faster, keeping customers happy, and reducing outages, all at once. Here’s where AI steps in: it spots congestion before it gets bad, sorts out faults before anyone even notices, tweaks radio settings on the fly, and takes care of support tickets automatically. Managing the network gets quicker, more reliable, and way easier to scale up.
At Avenga, we help telecom operators handle subscriber data, personalize services, automate billing, and ensure accurate revenue tracking with tailored BSS solutions.
Cybersecurity and network resilience
The latest telecommunications trend is cybersecurity and network resilience. Today’s telecommunications networks have evolved beyond traditional “pipes” due to the increasing number of connected devices supported by 5G, IoT, and AI, as well as the growing use of software and associated APIs and vendors. As a result, operators have expanded their network infrastructure, along with the associated attack surfaces. To combat these threats, operators are moving away from traditional rule-based security models toward adaptive defense models that utilize AI threat intelligence platforms to detect anomalies in real-time. These models use extrapolated detection and response (XDR) to link threat signals across core, edge, and cloud environments, as well as all endpoints of the network.
Resilience is equally as important as prevention. Operators are developing rapid containment playbooks (segmentation and hardened identity controls) to ensure that one compromised system will not cause a domino effect of disruption across the country. In addition to those developments, the integration of privacy and AI governance as part of the product roadmap is becoming increasingly prevalent, as the service is built on trust. The telecom providers that will emerge as winners are the ones that create new business models (such as premium enterprise connectivity and managed security) by demonstrating that their networks are designed to be secure as opposed to being repaired through security patches.
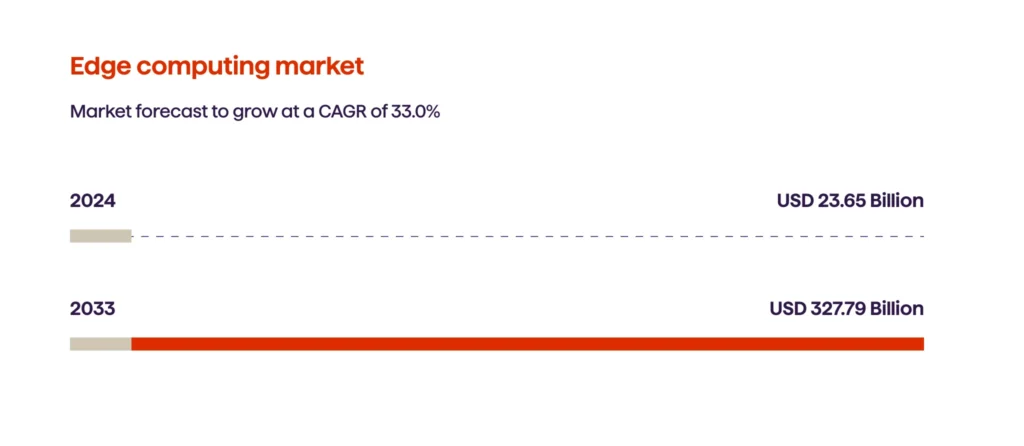
Edge computing and ultra-low latency services
By moving computation closer to where data is generated, Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) enables telecom providers to process data faster than ever before. The benefits for telecom operators are significant, as they can achieve ultra-low latency for AR/VR applications, real-time gaming, intelligent factory automation, and many other use cases, while also reducing their overall backhaul and network congestion.
The growing influx of real-time data created by IoT fleets is a continuing trend. Businesses want instant results from that data; consequently, 5G technology makes large-scale edge deployments a reality. This is changing the way operators conduct business: they can create strategic alliances to offer a full suite of edge services to their partners; sell superior-quality, low-latency services as a premium offering; and drive their customers’ digital transformation processes. However, distributed security, increased infrastructure costs, and operational complexity all come into play with every additional edge node deployed.
Open RAN and vendor diversification
Open RAN is revolutionizing the way operators manage their radio networks. They’re no longer locked into one vendor for every single piece. Now, they can select radios from one supplier, software from another, and run the entire system on standard servers. Everything connects through open interfaces, so it actually works together. This setup enables operators to roll out new features more quickly, scale up or down as needed, and gives them greater power to negotiate on price and future upgrades.
You can see this playing out with Rakuten Mobile in Japan. They’ve built a vast, cloud-native Open RAN network. Vodafone and Telefónica are also pushing ahead, running pilot projects and real deployments with gear from multiple vendors. The big win? Operators get more efficient and agile operations. The downside? There’s a lot more work involved in putting everything together and ensuring it all runs smoothly. But for many, that trade-off is worth it.
Fixed wireless access (FWA)
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) is transforming the telecom industry. Instead of tearing up streets to lay fiber, operators utilize the 4G and 5G towers already in place, along with a small device that is attached to your house or building. That’s how you get fast, low-latency internet, and you can usually set it up in just a few days. It’s way quicker than waiting months for someone to dig trenches.
For operators, FWA makes things easier. Installs are faster, there’s less construction, and the network team gets more control. They can boost 5G where it’s needed, combine different frequencies, and become more intelligent about how they manage traffic.
Where does FWA shine? First, in rural or remote areas, running cables is just too expensive. Second, in cities where people are tired of being stuck with slow DSL or cable. FWA steps in with speeds and prices that actually compete. So, whether you’re out in the sticks or in a crowded city, FWA brings real broadband to your door—no shovel required.
BSS/OSS modernization and a shift to microservices
BSS/OSS modernization redefines everything behind the curtain in telecom. It changes how new offers enter the market, how orders are processed, how problems are resolved, and how companies actually generate revenue. The old systems? They’re usually glued together and resistant to change. Now, operators are breaking things apart, rebuilding with open standards, and incorporating microservices and DevOps.
Telecom companies can use microservices to divide those big, complicated systems into smaller, easier-to-manage components, such as catalog, charging, provisioning, billing, and assurance. The payoff is practical: faster time-to-market for new tariffs and bundles, simpler maintenance, more reliable upgrades, and a smoother customer experience because “back office” bottlenecks no longer dictate what the business can ship.
Private 5G and industry-specific networks
Private 5G is rapidly emerging as a significant development in the telecom industry, as it enables companies to have direct control over their networks. No more just hoping public networks are good enough. Factories, ports, hospitals, and universities can now deploy their own 5G spectrum, either shared or dedicated, set up their own core, and protect it however they see fit. They are therefore fully aware of the type of performance they might expect.
So, what’s the real payoff here? Manufacturers secure fast and reliable connections for their robots and self-driving vehicles. Logistics teams leverage live video analytics to ensure everything remains safe. Hospitals get secure, dependable mobility for their clinical staff. Even energy sites finally see the steady, predictable connections they’ve been missing. And for operators, private 5G isn’t just another way to sell bandwidth—it’s a chance to bundle in edge computing, managed security, service-level agreements, and more. Now, they’re not just selling raw connectivity. They’re building networks that actually meet the needs of each industry.
6G groundwork and the path beyond 5G
6G isn’t waiting for 5G to wrap up. Work on the next generation kicks off in 2026, not because we’re done with fast downloads, but because the next wave will demand a lot more. 5G will be operational for roughly ten years by 2030. Operators will be aware of what has worked, such as enhanced coverage, flourishing device ecosystems, and edge computing.
But here’s the thing: 6G isn’t just about speed. It’s about blending our digital and physical worlds in ways that feel authentic, always-on, totally immersive connections you can rely on. We’re talking next-level XR, holographic calls, and the “Internet of Senses,” where sight and sound, and eventually even more senses, start feeling like you’re truly there. If this actually rolls out on a big scale, it’ll change the way people get healthcare, learn, and work. Picture affordable video and XR doctor visits for everyone, or learning in a hybrid classroom that feels real, no matter where you are.
There’s also a sustainability angle: richer digital experiences can reduce travel needs and “dematerialize” specific products and services, lowering emissions and resource consumption, if networks and devices are designed to be energy-efficient from the outset.
FAQ
Final words: Enabling the next generation of telecom
By 2026, winning in telecom won’t come down to who has the biggest network. It’s about who runs the smartest one. Automation and AI are changing everything—network management is now a real-time game. You identify problems, make informed decisions, and implement fixes on the fly. Edge computing and private 5G are finally delivering services that match people’s needs in the moment, rather than relying on outdated backbones.
Open RAN and the modernization of BSS/OSS are making it easier for operators to connect, optimize, and launch new services quickly, without complicating the process. And sure, 6G isn’t here yet, but the industry’s already laying the foundation. So here’s the real question for telecom leaders: Are you out there shaping what’s next, or just scrambling to keep up?
Interested to learn more about emerging trends in the telecom sector? Contact Avenga, your trusted technology partner in the telco industry.