Data Horizons: Exploring the Future Landscape of Big Data

April 28, 2025 19 min read
Navigating the transformative world of Big Data: from current trends to future prospects.
In an era where data is often called the new oil, understanding the vast expanse of Big Data becomes essential for any forward-thinking entity. Initially, Big Data emerged as a powerful technology that could solve complex problems without much fanfare or hype. Only after its capabilities became widely recognized did “Big Data” become a buzzword. This transition underscores the evolution of Big Data from a technical solution focused on handling large volumes of data at high speeds and in various formats to a critical element in operational and strategic decision-making across numerous industries.
The emphasis of many companies has shifted from merely acknowledging the size, speed, and diversity that Big Data offers, to actually leveraging its potential in many areas, which includes informing and driving business strategies. This reflects a maturation in general understanding and application of Big Data technologies.
This article investigates the current state of Big Data. It explores the technological advancements shaping its landscape, shows how Big Data is often used, and anticipates the potential future trends defining its trajectory.
The Current State of Big Data
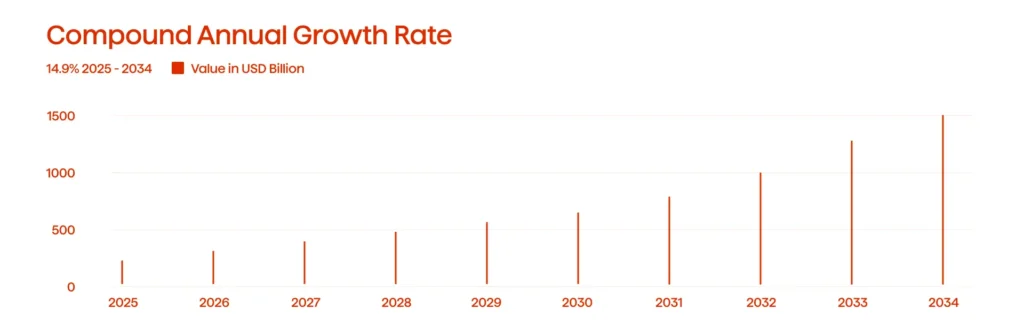
At the moment, the size of the Big Data analytics market is reaching $358 billion. Notably, by 2032, the market is expected to grow to $946 billion (see Figure 1) with a Compound Annual Growth Rate at 14.9%. So, it is safe to say that Big Data will not just continue to be popular, but it will experience a bright and exciting future.
The realm of Big Data has seen significant advancements and widespread adoption across various industries, profoundly impacting how businesses operate and strategize. Here’s an in-depth look at the current state of Big Data in some key sectors.
Healthcare
Healthcare has been a significant beneficiary of Big Data. Predictive analytics, driven by vast amounts of patient data, have enabled more personalized and preventative healthcare approaches. Integrating Electronic Health Records (EHRs) offers comprehensive patient health insights, significantly improving diagnosis and treatment processes.
According to McKinsey, healthcare systems like Kaiser Permanente have fully implemented solutions like HealthConnect to ensure data exchange across all medical facilities. As a result, Big Data brought improved outcomes in cardiovascular disease and an estimated $1 billion in savings from reduced office visits and lab tests. The Big Data healthcare market is expected to grow, with key players like IBM, Oracle, and GE Healthcare.
Finance
In Finance, Big Data is being used everywhere, from robust fraud detection to risk management. Financial companies often use it to develop personalized financial advice, tailored to individual customer data. And Big Data used for real-time data analysis when doing high-frequency trading helps to greatly reshape the trading arena.
Retail
Retail, a sector susceptible to consumer preferences, utilizes Big Data for personalized marketing, inventory optimization, and trend forecasting, among other things. This data-driven approach enhances customer experiences and operational efficiency.
Challenges in the Big Data Landscape
Despite its numerous benefits, the Big Data landscape faces multiple dilemmas, and some of them are:
- Data privacy and protection. Data privacy remains a significant concern with regulations like the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The need to balance data utility with individual rights is paramount.
- Security threats. The nature of Big Data (volume, distributed nature of data, etc.) adds additional issues to data protection, which necessitates robust security measures in order to protect sensitive data.
- Data quality. Ensuring data quality characteristics like accuracy, completeness, and consistency remains a key focus, especially with the growth in the volume of unstructured data.
While Big Data continues to reshape industries, addressing these challenges to harness its full potential is essential. Techniques and strategies have been developed to tackle these challenges, which are constantly revisited and enhanced. The distinct characteristics of Big Data make advancements in these areas interesting Computer Science research topics.
Technological Advancements Shaping the Future of Big Data Collection
The environment of Big Data is continually evolving, driven by groundbreaking technological advancements. These developments are enhancing how we handle large data sets and transforming the future of data analysis and management.
1. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in Big Data
The fusion of AI and ML with Big Data is a game-changer, heralding a new era of data analysis and business intelligence. These technologies enhance existing processes and open up unprecedented data handling and insight possibilities. Below are some of the most interesting AI/ML and Big Data integration possibilities:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP). NLP, a subset of AI, transforms data interaction and analytics. It allows machines to understand and interpret human languages, making data more accessible and insights more intuitive. This advancement is pivotal in managing and analyzing unstructured data, which forms a significant portion of Big Data.
- Automated ML (AutoML). Democratizing data science, AutoML facilitates automatic model selection and training. It lowers the entry barrier for data analysis, allowing more businesses to leverage Big Data without needing extensive data science expertise.
Integrating AI and ML in Big Data is not just a trend but a foundational shift. This integration empowers organizations to harness their data’s full potential, driving more intelligent decisions, innovative solutions, and competitive advantages.
2. Cloud Computing and Processing Data
Cloud computing is a cornerstone for Big Data processing and storage, offering scalable, agile, and cost-effective solutions. Its synergy with Big Data enables businesses to navigate the complexities of data management more efficiently than ever.
- Hybrid cloud environments. Balancing cloud scalability with on-premise data control, hybrid cloud environments are becoming increasingly popular. They offer the flexibility and scalability of cloud data storage and processing while allowing sensitive data to remain on-premise, thus addressing concerns like privacy and security.
- Big Data as a Service (BDaaS). This model offers scalable and cost-effective data solutions. BDaaS provides businesses access to Big Data technologies without the substantial upfront investment in infrastructure, making Big Data analytics more accessible to a broader range of companies.
- Integration with Serverless Computing. Serverless computing allows businesses to focus on data analysis rather than infrastructure management. It supports the Big Data ecosystem by providing a more straightforward and often more organized and cost-effective way to process and analyze large data sets.
The convergence of cloud computing with Big Data is a significant leap forward in data management and analysis. This technological amalgamation is shaping the future of data, offering enhanced scalability, security, and efficiency in handling large data sets.
3. Internet of Things (IoT) and Big Data
IoT is a critical driver in the evolution of Big Data, bringing a wealth of information through the processing and analysis of connected devices. Integrating IoT with Big Data analytics unlocks new opportunities for data-driven insights in various sectors.
- Sensor data analysis. IoT generates vast amounts of sensor data. Analyzing this data provides actionable insights, such as predicting equipment maintenance needs, enhancing user experiences, and optimizing processes.
- Smart Cities and IoT. Leveraging Big Data for urban development and management, smart cities use IoT sensor data to enhance the various aspects of urban life, including traffic management, energy use, and public safety.
- Challenges in data integration. One of the primary challenges in the IoT and Big Data space is integrating data from disparate IoT sources. Ensuring data quality, consistency, and actionable insights from these diverse data sources requires sophisticated data processing and management strategies.
The intertwining of IoT with Big Data is a testament to the growing need for interconnected systems and advanced data analytics. As IoT expands, its role in shaping the future of Big Data and influencing decision-making processes across industries becomes increasingly significant.
Big Data management, therefore, is becoming more sophisticated and is ensuring better data quality, enhanced data security, and more coherent data processing. These advancements underscore the dynamic nature of the data space, heralding a Big Data revolution, reshaping industries, and redefining the future of data.
Future Trends in Big Data Analytics
As Big Data continues to expand and evolve, future trends indicate a significant transformation in how data is processed, analyzed, and secured. These developments promise further integration of Big Data into the core of business operations, providing, among other things, deeper insights and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
1. Predictive Analytics
Predictive Analytics in Big Data is transforming how organizations approach forecasting and decision-making. By leveraging advanced models and data-driven insights, businesses can predict future trends and behaviors with unprecedented accuracy, leading to more informed and strategic decisions.
- Advancement in forecasting models. Integrating diverse datasets for more accurate predictions is a crucial trend. This advancement empowers businesses to utilize Big Data for strategic forecasting, enhancing their ability to predict market trends and consumer behaviors more accurately.
- Predictive maintenance in industries. Using Big Data for predictive maintenance allows industries to preempt equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Customer behavior prediction. Businesses can significantly improve customer engagement and conversion rates by tailoring marketing strategies to data-driven insights.
The advancements in predictive analytics signify a future where Big Data is not just about handling large volumes of information, but also about deriving proactive insights that can drive business growth and operational efficiency.
2. Real-Time Data Processing for Data Scientists
Real-time data processing has been a longstanding practice within the Big Data landscape. It is integrated into a growing number of use cases across various companies. This integration continues to expand, allowing businesses to respond swiftly to market changes and customer interactions, cementing agility and quick decision-making as essential competitive advantages.
- Stream analytics. Harnessing data streams for immediate decision-making is becoming increasingly a high priority. This real-time analysis enables businesses to respond swiftly to market changes and customer needs.
- Real-time data in financial markets. The impact of real-time data on trading and risk management in financial markets is profound, necessitating advanced analytics and processing capabilities.
- Challenges in real-time data processing. Addressing issues like latency and computational needs is essential in order to leverage the full potential of real-time data processing.
Real-time data processing helps redefine the pace and consistency of how businesses operate, making instantaneous data analysis and decision-making a new norm in the data-driven world.
3. Enhanced Data Privacy and Security
In the current era of Big Data, enhanced data privacy and security have become paramount. With the increasing importance of safeguarding sensitive information, businesses are adopting advanced technologies and adhering to stringent regulations so as to protect data integrity and maintain customer trust.
- Advanced encryption techniques. Protecting data in transit and at rest is becoming even more critical with the increasing volume and sensitivity of the data being handled. Advanced encryption techniques are essential for safeguarding this data.
- Federated learning. This innovative ML approach enhances privacy and security by limiting data exposure. It permits model training on decentralized devices, maintaining data confidentiality effectively. By distributing the training process across individual devices while keeping the data on local devices or servers instead of uploading the entire data set to a central server for training, sensitive data remains less exposed and thus more secure while still allowing for collaborative learning.
- Regulatory compliance. The increasing focus on data protection laws, such as the GDPR, necessitates that businesses adapt to these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maintain customer trust.
The emphasis on enhanced data privacy and security marks a significant shift in the Big Data arena, where protecting sensitive information is as crucial as deriving insights from it. This trend towards greater security and compliance is fundamental in maintaining trust and integrity in the burgeoning world of Big Data.
Big Data Trends in Emerging Technologies
Big Data has become a cornerstone for innovation and advancement. As we look into emerging technologies, we witness a remarkable synergy between Big Data and cutting-edge technological paradigms such as blockchain, quantum computing, and edge computing.
Each of these technologies redefines the potential and scope of Big Data and sets new standards for competence, security, and analytical power. This exploration into how Big Data intertwines with these emerging technologies offers a glimpse into a future where the boundaries of data processing and security are continually expanded and reimagined.
1. Big Data and Blockchain
Integrating Big Data with blockchain technology is a groundbreaking development, offering enhanced security, transparency, and proficiency in data management. This combination revolutionizes data storage, access, and audits across various sectors.
- Enhancing data traceability and transparency. Blockchain’s ability to create immutable and transparent audit trails transforms data traceability. This feature is particularly crucial in sectors where data integrity and history are paramount.
- Smart Contracts for data sharing. Using blockchain-enabled smart contracts automates data access and usage agreements, ensuring compliance and efficiency in data transactions.
- Decentralized data marketplaces. Blockchain facilitates the creation of decentralized data marketplaces, allowing secure and transparent data exchanges while enhancing trust in those data transactions and collaborations.
Blockchain’s impact on Big Data is multifaceted, providing solutions that secure data transactions and enhance the overall trust and potency in digital ecosystems.
2. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing represents a significant leap forward in processing capabilities, with profound implications for Big Data analytics, cryptography, and ML.
- Quantum algorithms for Big Data. Quantum computing introduces new paradigms into data processing, enabling the handling of complex data sets at unprecedented speeds and efficiencies.
- Impact on cryptography. Quantum computing confronts the current encryption methods, necessitating the development of quantum-resistant cryptographic techniques.
- Quantum-enhanced ML. The immense processing power of quantum computers offers potential advancements in ML, particularly in complex data pattern recognition.
As quantum computing evolves, its impact on Big Data processing and security will probably be very significant, unlocking new capabilities and challenges in data analysis and protection.
3. Edge Computing
Edge computing is reshaping the data processing landscape by bringing computation closer to data sources, thereby significantly reducing latency, optimizing network bandwidth, and enabling faster decision-making.
- Reducing latency. By processing data closer to its source, edge computing drastically reduces latency, while at the same time enhancing the efficiency of real-time data applications.
- Edge AI. Integrating AI at the edge enables faster insights and intelligent decision-making directly at the data source.
- Network bandwidth optimization. Edge computing reduces the need for data transmission to central servers, optimizing network bandwidths and reducing related costs.
The rise of edge computing marks a paradigm shift in data processing, by offering a more distributed and often a more productive approach that complements traditional cloud-based systems. This trend is poised to play an essential role in the future of Big Data, especially in applications requiring real-time processing and analysis.
As we step into the future, the intersection of Big Data with these emerging technologies heralds a new era of possibilities and challenges. Integrating blockchain enhances trust and security; quantum computing is pushing the limits of processing power and data analysis; and edge computing is presenting a huge potential in real-time data processing for some situations.
Together, these technologies are transforming Big Data, marking the future of technology, driving innovation, and creating new opportunities across the various industries. The journey ahead in Big Data and these emerging technologies is one of continuous exploration, adaptation, and groundbreaking advancements.
Preparing for the future of Big Data
As we venture into an increasingly data-driven world, preparing for the future becomes multidimensional. Embracing Big Data and its related technologies requires a proactive approach to skill development, regulatory adaptation, and collaborative innovation. This preparation is about harnessing the potential of Big Data and creating a sustainable and ethical framework for its use.
Skill Development: Preparing Employees for a Data-Driven Future
In the face of rapidly advancing Big Data technologies, equipping the workforce with the necessary skills is essential. Initiatives focusing on data literacy, specialized training, and continuous learning are crucial for organizations to stay competitive and innovative.
- Emphasizing data literacy. Understanding data analysis and interpretation across all organizational levels is vital. As per a report by PwC, a growing number of job postings across all sectors now demand data proficiency, reflecting the growing importance of data skills in the modern workplace.
- Specialized training programs. Developing courses and certifications in Big Data, AI, and analytics is imperative. For example, IBM and Microsoft offer certification programs to upskill professionals in these domains.
- Bridging the skill gap. Collaborating with educational institutions to align curriculum with industry needs is significant. Initiatives like Google’s collaboration with universities for AI research and training, and many others, aim to bridge this gap.
- Continuous learning culture. Encouraging ongoing skill development to keep pace with technological advancements is crucial. Companies like Amazon, and many more, invest heavily in continuous learning programs for their employees.
Fostering a culture of continuous learning and inclusivity in tech education is imperative for organizations to effectively leverage Big Data and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Policy and Regulation: Shaping Guidelines for Responsible Data Use
As Big Data becomes integral to business operations, the need for comprehensive data policies and regulatory compliance is more pronounced. Establishing data privacy, ethical usage, and governance standards is pivotal for maintaining trust and integrity in data-driven practices.
- Global data privacy standards. Understanding and implementing GDPR, CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), and other international data protection laws is vital. According to Gartner, by the end of 2024, 75% of the world’s population will have personal data covered under modern privacy regulations.
- Ethical data usage frameworks. Developing internal policies for honest data collection, storage, and use is essential. McKinsey emphasizes the importance of ethical data usage as a core component of digital trust.
- Adapting to emerging tech regulations. Staying ahead of regulatory changes in AI, IoT, and other emerging technologies is paramount. The European Union’s Digital Services Act and Digital Markets Act are examples of such evolving regulations.
- Public-private partnerships in policymaking. Collaborating with governmental bodies to shape balanced data policies is essential. For instance, the partnership between IBM and the U.S. government on AI ethics is a step in this direction.
- Data governance best practices. Establishing clear guidelines and accountability for data management within organizations is imperative. Deloitte’s insights on data governance highlight the need for robust frameworks in the age of Big Data.
Navigating the complex terrain of data policies and regulations requires a concerted effort from private and public sectors to ensure that data is used responsibly and ethically.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Fostering Innovation Through Cooperation
In the realm of Big Data, collaboration and partnerships across various sectors are critical drivers of innovation and growth. By sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise, organizations can unlock new opportunities and tackle complex matters in the data space.
- Industry-academia collaboration. Leveraging academic research and innovation in commercial applications is crucial. Partnerships like the one between Stanford University and Google on ML research are exemplary.
- Cross-industry alliances. Sharing knowledge and resources across different sectors to drive innovation is essential. The Data Collaborative for COVID-19, a partnership among tech companies, health organizations, and governments, is a notable example.
- Open source and community projects. Contributing to and benefiting from the open-source community accelerates innovation. Projects like Apache Hadoop and TensorFlow are a testament to the power of community-driven development.
- Global data sharing initiatives. Participating in international projects for data sharing to solve global problems is significant. One example is the Global Open Data for Agriculture and Nutrition (GODAN) initiative, which uses open data to solve critical food security challenges.
- Incubators and accelerators for data startups. Supporting the growth of startups focusing on Big Data and analytics is vital for fostering new ideas and technologies.
The future of Big Data is inherently linked to collaborative efforts that span industries, disciplines, and borders. These partnerships fuel innovation and ensure that advancements in Big Data are inclusive, ethical, and beneficial to a broader spectrum of society.
As we stand on the brink of a new era defined by Big Data, preparing for the future involves a holistic approach encompassing collaborative innovation, skill development, and policy adaptation. The journey ahead is not just about mastering the technical aspects of Big Data, but also about fostering an environment where continuous learning, ethical data practices, and cooperative innovation are ingrained into the fabric of our technological advancement.
This comprehensive readiness will enable us to harness the full potential of Big Data, driving forward a future that is not just data-driven, but responsible, inclusive, and sustainable. As Big Data continues to redefine the boundaries of possibility, our preparedness today will shape the success of our data-driven tomorrow.
Takeaways
As Avenga navigates the vast landscape of Big Data, it’s important to note that our journey has been a high-level exploration. We’ve focused on specific areas of interest to us and have dug into selected industries and use cases within the realm of Big Data, however, we acknowledge that there is a wide array of industries and numerous Big Data cases that we have not covered in-depth.
Avenga has also looked at the technological advancements shaping Big Data’s future and the trends poised to redefine its trajectory. Big Data stands at the forefront of a technological revolution. It’s transforming many sectors, including healthcare, finance, and retail. This revolution also has groundbreaking implications for other IT areas like AI/ML, cloud computing, and IoT.
The future trends in predictive analytics, real-time data processing, and enhanced data privacy and security illuminate the path toward a more insightful, agile, and secure data-driven future.
Contact Avenga to embark on a journey towards harnessing the transformative power of Big Data. Let us help you turn data into actionable insights and strategic decisions, propelling your business toward unprecedented success in the data-driven era.



