AI and Pharma Trends 2025
May 6, 2025 12 min read
AI has become the talk of the town, no matter the industry. Recent advancements in this technology have turned the impossible into reality.
It enables human experts to focus on the most critical, high-value tasks while delegating mundane work to smart technology, unlocking new growth opportunities and accelerating time to market. This is supported by evidence. New use cases made possible by AI have the potential to greatly enhance production KPIs, resulting in increases of up to 10% in time to market and up to 25% in revenue. Another resource says AI is now being used for drug discovery by 80% of specialists in the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries. Further, by the end of 2025, pharmaceutical businesses may generate between $350 billion and $410 billion in value annually from AI applications.
Delve deeper to uncover the key trends shaping the future of the pharmaceutical industry. Explore how new technology trends are helping to overcome significant challenges. Let’s take a peek behind the curtain to discover what biopharma companies will be up to in 2025.
Agentic Artificial Intelligence Redefines Life Sciences
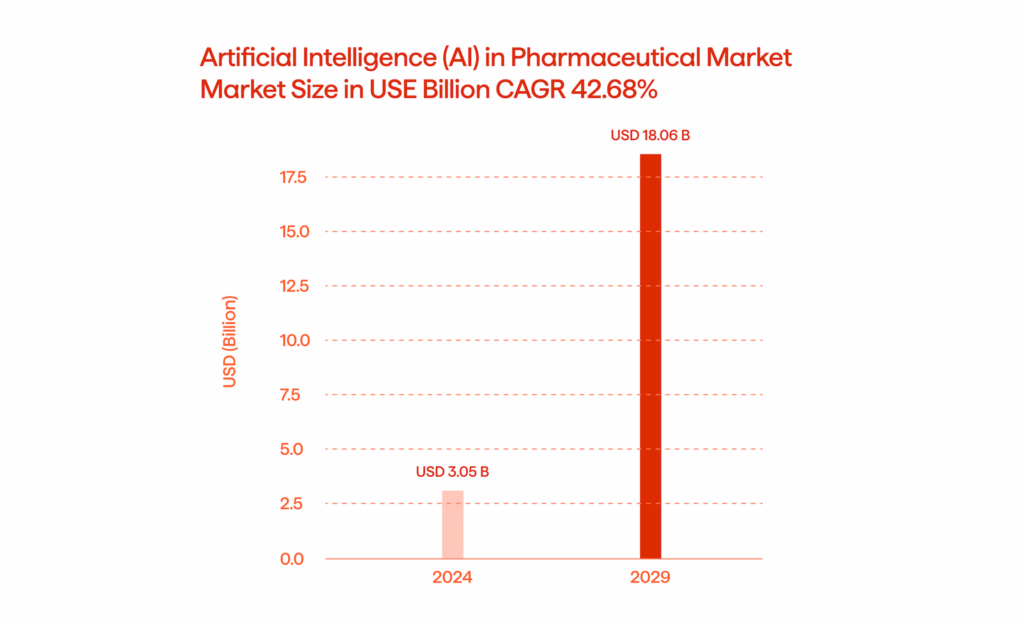
The pharmaceutical sector is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 42.68%, from USD 3.05 billion in 2024 to USD 18.06 billion by 2029. Technological advancements in AI for clinical trials, drug discovery, and operational efficiency are the key drivers behind this rapid expansion.
By 2027, Gartner predicts that 30% of top life sciences organizations will leverage generative AI-generated synthetic data to enhance their digital twin initiatives, revolutionizing how organizations use data to simulate and refine drug development processes. This technology will augment existing datasets and significantly improve in silico modeling. Additionally, non-technical barriers, such as poor culture integration and governance gaps, are expected to account for 40% of generative AI project failures, highlighting the need for robust strategies and adoption frameworks to fully capitalize on AI innovations.
One of the most common applications of AI is agents. Since agentic AI is the new buzzword, it’s no surprise that it is also making an impact in pharma, especially in light of the changes COVID-19 has brought to the industry. Just five years ago, pharmaceutical companies were hesitant to adopt AI, but everything has shifted with the increasing need to provide more efficient customer service and support.
However, there’s a key distinction between generative AI and AI agents. While generative AI is useful for language-based tasks, its applications are limited. AI agents, on the other hand, are multifunctional. For example, they can enhance end-to-end planning and execution processes, which typically take anywhere from six months to a year and a half to complete. AI agents can reduce this time frame to as little as four or five months.
How is this possible? First, there’s no need to manually analyze spreadsheets (which, by the way, can take months!). In just a few days, brand managers can evaluate AI-generated scenarios that assess the effectiveness of broadcast, digital, and in-person campaigns. These recommendations include thorough justifications and anticipated outcomes, resulting in faster and more informed decision-making.
Secondly, agentic AI impacts provider segmentation and targeting by integrating various data streams, including practice features, patient demographics, and behavioral patterns. This data enables the creation of more accurate segmentation models much faster, with continuous updates based on real-time data. This marks a significant advancement over previous methods.
Additionally, agentic AI revolutionizes field force planning by instantly optimizing resource allocation, territory structure, and sales force size. Thousands of variables are evaluated in real-time to adapt dynamically to market shifts, including drive duration, account value, and representational capacities. This allows pharma companies to sustain productivity throughout the year and ensure that resources are used efficiently.
One important point to note, however, is that while agents play a key role in process automation, service providers should remain the final decision-makers. For instance, human strategists still determine market positioning and strategic investments, even though AI agents can quickly assess market data and recommend resource allocation.
Precision Medicine Takes Center Stage In Medical Innovation
First of all, let’s begin with a definition. The Precision Medicine Initiative defines precision medicine as “an emerging approach for disease treatment and prevention that takes into account individual variability in genes, environment, and lifestyle for each person.” With this method, medical professionals and researchers will be able to more precisely forecast which preventative and treatment approaches for a certain illness will be effective for specific populations.
This key trend for 2025 radically rethinks healthcare delivery. Instead of a one-size-fits-all approach, it focuses on therapies tailored to each patient’s genetic composition, environment, and lifestyle. Rapid advances in biomarker discovery, genetic sequencing, and AI-driven analytics are driving this innovation, allowing practitioners to provide highly targeted treatments.
In oncology, precision medicine enables physicians to identify the specific mutations causing cancer in a patient’s tumor, facilitating treatments like immunotherapies that enhance the body’s immune response to cancer cells, or targeted therapeutics (e.g., HER2 inhibitors for breast cancer). Compared to traditional chemotherapy, these personalized treatments improve efficacy while significantly reducing side effects.
The potential of precision medicine is further enhanced by AI and machine learning. These technologies are the rockstars of data analytics. They enable analysis of enormous datasets, including genomic and electronic health records, to find trends and forecast treatment outcomes. AI can reduce trial-and-error prescribing and improve results by stratifying patients into groups most likely to benefit from a new treatment.
Gen AI Transforms Patient Engagement And The Customer Experience
Efficient provider-patient communication is the cornerstone of the healthcare and pharmaceutical industry. Those pharma leaders who want to stay on top of the market must prioritize digital technologies that streamline communication, foster patient engagement, and deliver personalized experiences. This is where Gen AI takes center stage.
Its use cases are virtually limitless. AI-driven chatbots are gaining momentum. By analyzing customer data, they can efficiently answer patient questions, provide notifications for taking medicine, and even offer personalized health recommendations. Plus, it can be used to communicate the effects of prescribed medicine in a clear and understandable way, explain the nuances of a clinical trial, and provide culturally relevant educational materials, such as films or booklets, tailored to the language and health literacy of various regions. Interestingly, this technology can also be used to suggest treatments or health plans concerning cultural norms and religion-based dietary restrictions, ensuring all patients feel heard and respected.
Generative AI Success Personified
We’ve helped copious pharma and life sciences companies easily adopt generative AI for optimized clinical trials, efficient cost-saving, and accelerated drug discovery. Learn the practical cases in our dedicated whitepaper. Get the whitepaper
Release And General Availability Of Salesforce Life Sciences Cloud For Customer Engagement
Salesforce recently announced the upcoming release and general availability of the Life Sciences Cloud for Customer Engagement, a dedicated platform designed to revolutionize patient and healthcare professional (HCP) engagement. The platform integrates with the Salesforce ecosystem. It offers tools to match patients with clinical trials, manage patient data, and deliver personalized interactions.
Salesforce’s Life Sciences Cloud is a game-changing platform designed to enhance patient and healthcare professional (HCP) engagement. Powered by generative AI and the Agentforce tool, it goes beyond streamlining customer interaction. Agentforce enables dynamic resource allocation, sales force optimization, and personalized engagement strategies. Additionally, the platform matches patients with clinical trials using an extensive ecosystem of patient data, accelerating recruitment processes and enhancing trial outcomes. Salesforce continues to double down on promoting Agentforce, reflecting its growing relevance in modernizing pharma industry operations .
Advancements In Genomic Medicine And CRISPR Technology
Although genomic medicine has undergone significant technological advancements in recent years, 2025 marks the dawn of a true revolution in the field.
Cracking an individual’s genetic code allows medical professionals to provide personalized diagnoses and treatments that go beyond basic techniques. Take cancer, for example, and its tumor profiling. Genomic medicine identifies genetic abnormalities that enable more targeted treatments, such as HER2 (Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2) inhibitors for breast cancer or PARP (Poly-ADP Ribose Polymerase) inhibitors for ovarian cancer.
The gene-editing marvel CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) takes precision DNA alteration to new heights. Its ability to edit DNA with surgical accuracy is transforming medical norms. CRISPR’s impact is revolutionary, from correcting genetic mutations that cause sickle cell anemia and cystic fibrosis to enhancing immune cells in CAR-T treatments aimed at eradicating cancer.
Together, CRISPR and genomic data are reshaping our understanding of gene therapy. While CRISPR acts as the tool for editing or replacing defective genes, genomic data identifies the precise sites for intervention. This powerful combination is accelerating drug discovery, enabling the development of accurate disease models and speeding up the creation of next-generation treatments. For example, CRISPR-based tailored shots are being developed to precisely target genetic markers associated with infectious diseases and cancer.
Expansion Of Direct-to-consumer Models
Industry leaders are increasingly leveraging direct-to-consumer models, driven by consumers’ growing demand for better, more personalized interactions. The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed this shift, accelerating the adoption of digital platforms, wearable health monitoring devices, and telemedicine.
According to a 2023 Journal of American Marketing study, almost three out of four patients look for providers online. Another study revealed that even drug reviews from consumers can help assist patients in locating prescription drugs that suit their needs. All these changes are inevitable. Just imagine—a patient accustomed to monitoring their critical health indicators via smartphone is unlikely to revert to the inconvenience of scheduling in-person provider visits. They are far more likely to prefer remote consultations and doorstep drug delivery—a modern, convenient, and highly personalized approach.
The Rise Of The GLP-1 Weight Loss Boom
Ozempic was one of the best-selling drugs of 2023. Since other GLP-1 drugs are becoming more popular in treating obesity and diabetes, some analysts believe the market can reach $100 billion or higher by 2030. The growing popularity of modern obesity treatments has sparked a secondary market for supportive services and products aimed at improving patient outcomes.
Despite the growing popularity and proven benefits of GLP-1 medication, prescription coverage remains limited. In the employer insurance market, coverage has seen some growth, with about 34% of employers offering coverage for both weight loss and related disabilities. Many companies are capitalizing on supplementary services, such as Weight Watchers’ customized diet plans, GNC’s newly launched support section, and Daily Harvest’s GLP-1 companion food collection, which operates as a subscription service.
Global Pricing Pressures And The Evolving Regulatory Landscape Challenge Innovation
With healthcare costs under increasing international scrutiny, governments and payers are implementing stricter price controls and reimbursement policies. Although the goal of these policies is to reduce the cost of pharmaceuticals, they usually result in a reduction in the margins needed for research and development expenses. The sustainability of future inventions may be impacted by initiatives such as the Inflation Reduction Act, which encourages price negotiations on expensive pharmaceuticals in the United States.
Another significant challenge is the growing number of pharmaceutical regulations. These regulations align well with the increasing adoption of AI and other agile technologies. New recommendations from organizations like the FDA and EMA are being released to address emerging therapies involving biologics and gene editing. While these regulations are crucial for ensuring safety and effectiveness, they also add complexity and costs to the drug development process. Managing international compliance standards for a single treatment can delay its market release, which may deter investment in innovative research.
Commercialization Changes Driven By AI And GenAI
It’s no surprise that recent advancements in AI and ML are transforming how medicine is brought to market. Today, AI helps organizations gather data on patient needs, forecast demand for new therapies, and guide distribution and manufacturing plans with exceptional precision. Furthermore, generative AI enables coordinated marketing efforts that resonate more effectively with target audiences, including payers, healthcare providers, and patients, significantly increasing engagement and conversion rates.
Pricing tactics are also evolving. Consequently, AI models construct value-based price models by analyzing large data sets, including competitor pricing, income level, and treatment outcome. This effectively matches the cost to the therapy’s benefit and improves a business’s negotiating position with regulators and insurance. That being said, these are the three ways in which artificial intelligence impacts commercialization in pharma:
- Market analysis. It predicts demand and optimizes production based on advanced analytics.
- Personalized marketing. It tailors campaigns to individual audiences for better engagement and personalization.
- Pricing strategies. It optimizes pricing based on comprehensive data.
Pharmaceutical Sector 2025: More To Come
To sum up, AI has taken the central stage in pharmaceutical innovation, accompanied by CRISP technology, direct-to-consumer models, and Salesforce. Each of these trends is anticipated to shape the future of healthcare in the upcoming years. Personalization is among the major advancements. Patients these days are seeking tailored experiences, so companies need to take their preferences into account when building their strategies.
Interested to learn more about pharma trends and how leading companies are keeping pace? Want to learn how to achieve significant growth in these changing market conditions? Contact Avenga.



