Key Applications Of IoT For Automotive
May 9, 2025 10 min read
The impact of IoT on the automotive industry has been profound. In this post, we will discuss its key applications in the industry and provide tips for implementing IoT automotive projects.
To gain a competitive edge in the dynamic landscape of the automotive industry and meet the evolving expectations of consumers, automobile companies are increasingly harnessing the transformative capabilities of automotive IoT (Internet of Things). The connectivity that IoT provides plays a pivotal role in optimizing the entire car manufacturing process by providing invaluable insights and facilitating efficient decision-making.
The applications of IoT in the automobile industry have left an indelible mark on the sector, transforming the way people perceive and interact with their vehicles. In essence, the potential that IoT brings to the automotive sector is vast, and it is revolutionizing commuting patterns and redefining the relationship between individuals and their vehicles.
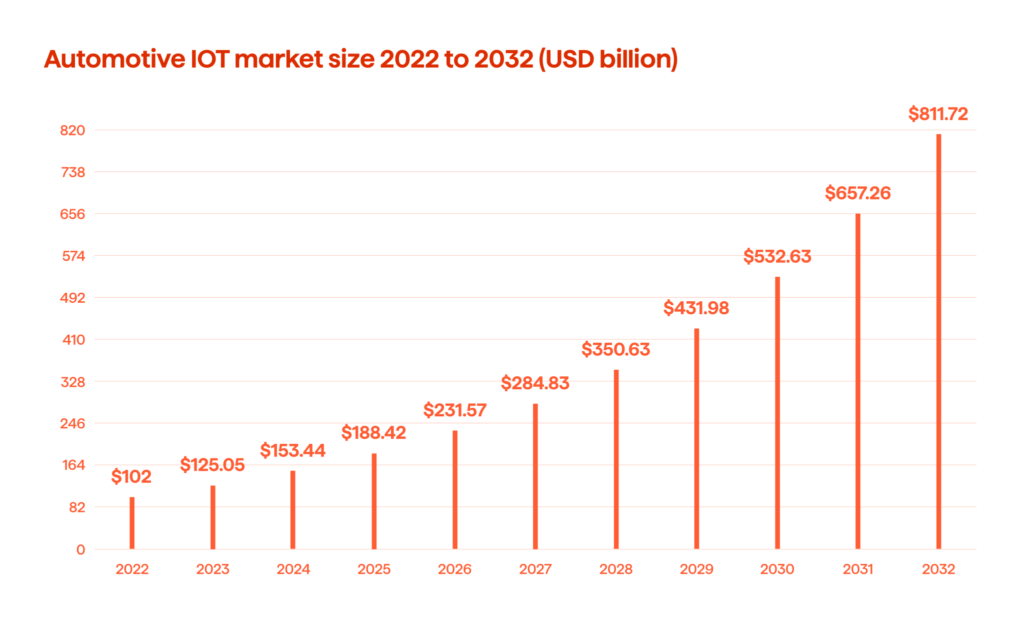
The global automotive IoT market size was valued at USD 102 billion in 2022 and is projected to surpass USD 811.72 billion by 2032 (Fig. 1). The trajectory of the automotive sector is undeniably being shaped by the rapid integration and adoption of automotive IoT, which is heralding an era of innovation and unparalleled connectivity in the world of automobiles.
[Image Source ]
The Key Ways Companies Are Implementing Automotive IoT
Connected infotainment. Modern vehicles are equipped with information and entertainment systems that are connected to the internet via built-in cellular connectivity. This allows for smart infotainment features such as listening to internet radio, integrated apps for finding parking spaces, making restaurant reservations, checking weather updates, receiving traffic alerts, and so on. The connected systems receive over-the-air software updates to continuously upgrade functionality.
Vehicle telematics. IoT connectivity allows real-time monitoring, tracking, and diagnosis of vehicles. Fleet managers can track vehicles, driver behavior, and vehicle health using telematics services. It improves fleet management, safety, and scheduling operational efficiency. Insurance providers also use driving data for customized policy pricing.
Learn more about how we developed an advanced end-to-end fleet management system for Intel. Success story
Smart mobility solutions. The data insights from connected vehicles inform municipal planning thereby helping to reduce congestion and pollution. It also enables usage-based insurance, smart parking solutions, and other services that aim to improve mobility.
Enhanced customer experience. Connectivity allows automakers to gather data on customer usage patterns and issues in real-time. It provides personalized services and support to vehicle owners over their lifetime ownership. Customers benefit from over-the-air software enhancements, proactive communications, and contextual engagement.
New business models. IoT is enabling new business models like vehicle-sharing and transportation-as-a-service. It is transforming automakers into mobility providers beyond just selling vehicles. Big tech firms are also entering the mobility space by leveraging their expertise in data management, IoT, and Machine Learning (ML).
How Companies Should Approach An Iot Automotive Project
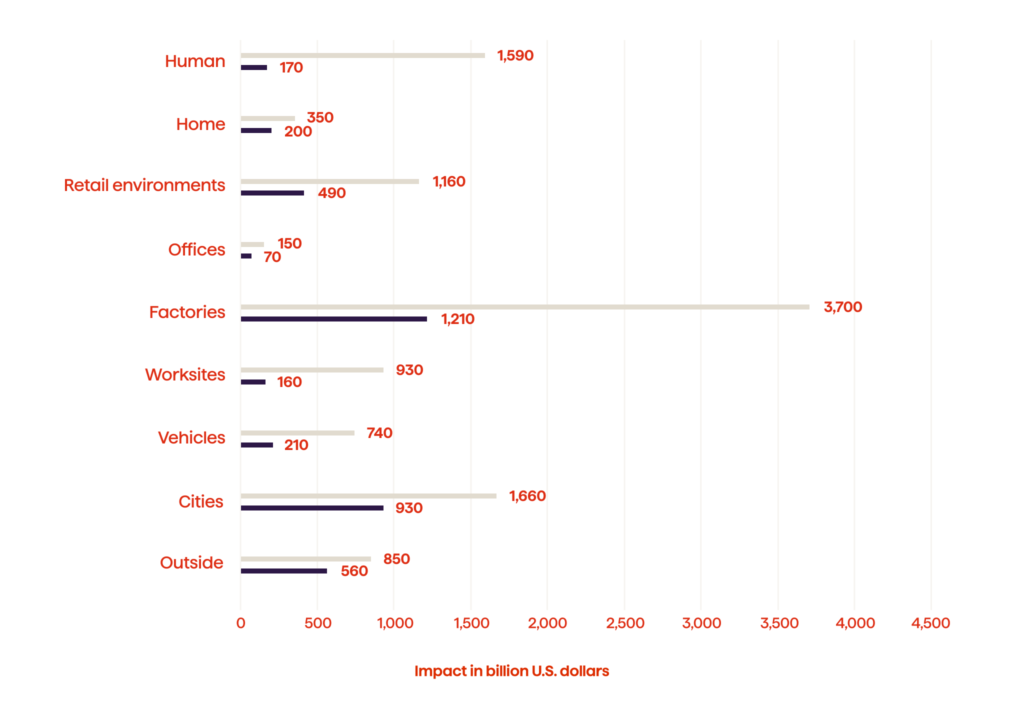
IoT is gradually becoming widespread. As per Statista’s projections, the anticipated investment in automotive IoT is poised to achieve a staggering $740 billion by the year 2025 (Figure 2.) And yet, it doesn’t come without its challenges. In fact, some research states that as many as 75% of IoT projects aren’t successful. So, here are some data-driven recommendations on how auto companies can successfully implement an IoT initiative.
[Image Source ]
Start with the business case. Every IoT project begins with identifying the specific business goals that IoT can help achieve. This could be boosting sales through connected services, reducing warranty costs via predictive maintenance, improving fleet utilization, enhancing customer experience, or other such objectives. A sound business case will identify the tangible metrics of success.
Assess IoT readiness. An organization should evaluate their IoT maturity across areas like connected products, data infrastructure, partner ecosystems and talent, as well as identify strengths to leverage and gaps to address. They can build internal capabilities and external partnerships as needed. Additionally, leaders can be appointed to drive their IoT strategy.
Take an ecosystem approach. Develop solutions jointly with technology vendors, connectivity partners, data providers and app developers, as no single firm can deliver the entire IoT value chain. It is advantageous to leverage these partners’ expertise and fill capability gaps through those alliances.
Implement a flexible technology architecture. The technology architecture must seamlessly integrate sensors, embedded systems, connectivity, cloud services and data analytics. An organization needs to make certain the interoperability between components is fluid as this allows for scalable deployment across vehicle models and geographies.
Enable secure data capture & analysis. Connected vehicles generate massive amounts of data. It is imperative that capabilities are built to securely collect, store and analyze this data through edge computing and cloud analytics in order to extract insights. However, data privacy concerns must be addressed proactively.
Develop differentiating use cases. Identify high-value IoT use cases that are tailored to customer needs and focus on delivering those excellently rather than trying to do everything at once. The initial use cases should provide quick wins and learnings in order to inform future initiatives.
Take an incremental approach. Given the many complexities involved, implement IoT features incrementally based on priorities rather than trying to overhaul systems completely. This agile approach de-risks the project and gathers invaluable feedback from initial deployments so as to enhance later rollouts.
Design for superior UX. IoT needs to blend seamlessly into the driver’s experience. The user experience (UX) design should minimize distractions and complexity while personalizing features and interactions. Voice assistants, recommendations, and proactive interfaces can provide a smart contextual experience.
Evaluate operational impacts. IoT solutions will transform services, maintenance, and dealer interactions. Assess the downstream operational changes needed to maximize benefits while minimizing business disruption. Train staff and partners fully on the new IoT-enabled processes.
Measure ROI continuously. Given the significant investments involved, continuous measurement of business impact vs. costs is crucial. Track relevant metrics like utilization rates, service costs, warranty claims and customer satisfaction, then refine the solutions based upon emerging data and business needs.
With careful planning centered on clear business goals, automotive companies can make IoT a competitive differentiator. But, they must take an ecosystem approach and implement incrementally while continuously measuring results. Managing change and talent development are also critical in order to maximize the benefits of IoT in the long run. The opportunities for value creation are enormous for the auto firms who can successfully deliver connected intelligent experiences.
Important Considerations When Using IoT For Automotive
While bringing many benefits, IoT also raises concerns around data privacy, system security, and over-reliance on technology. Automakers and tech partners need to ensure secure data handling and provide adequate fail-safes in these connected systems. Overall, IoT is bringing cars closer to the vision of them becoming truly intelligent machines and transforming road transportation. The shift towards connected, autonomous, and shared mobility promises to be more sustainable and efficient if implemented responsibly by automotive stakeholders.
- Technical complexity – Integrating sensors, connectivity, cloud platforms, data infrastructure and applications creates a complex system-of-systems. The lack of internal expertise in new technologies like the cloud and AI can impede progress. Learning how to build IoT applications is crucial for overcoming the technical complexities and ensuring successful implementation of automotive IoT solutions.
- Security risks – Connected vehicles are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Building comprehensive data security, access controls, and fail-safes requires rigorous approaches from the start.
- Data silos – Much of the data generated may reside in isolated legacy systems. Breaking down data silos so as to enable aggregation, analysis, and insights is difficult.
- Integration with legacy systems – New IoT solutions must integrate with existing vehicle electronics, in-house IT systems, and dealer networks. Integration challenges can delay rollouts.
- Large capital investments – IoT requires upfront investments in sensors, connectivity, cloud infrastructure, analytics tools, and talent. Securing adequate funding and ROI can be daunting.
- Long development cycles – Automotive product cycles are lengthy compared to software cycles. Aligning agile IoT development with slower vehicle development will prolong time-to-market.
- Organizational resistance – IoT brings new ways of working that may be hindered by inertia, and possible turf wars between IT and engineering teams. Change management is imperative in order to be successful.
- Lack of talent and partners – The skill sets required for IoT are in short supply. And, identifying the right external partners to work with also takes time and effort.
- Unclear ROI – With high upfront costs, mapping IoT benefits to concrete ROI over 3-5 year timeframes is difficult. Gaining stakeholder support for the investment will be challenging without clear ROI projections.
- Fragmented standards – Competing IoT platforms and protocols make device and systems integration complicated. The lack of standards also limits reusability across models or brands.
Any automaker embarking on an IoT initiative must adequately plan for and invest in mitigating these technology, process, and organizational concerns from the start to ensure a successful rollout.
Why Is It A Good Idea To Partner With An Experienced IoT Development Company For Your IoT Automotive Project?
Organizations without substantial experience in IoT implementation can massively benefit from partnering with a seasoned IoT vendor. Here are the key perks of such cooperation for an auto manufacturer.
- Access to IoT expertise – IoT requires diverse technical skills around embedded systems, connectivity, cloud, data analytics, and AI. A development partner brings cross-functional expertise that may not exist in-house.
- Faster time-to-market – An experienced vendor can help quickly build, integrate, and deploy IoT solutions using proven platforms and methodologies. It accelerates go-to-market versus internal development.
- Reduced costs – Outsourcing development to a specialist vendor reduces the upfront capital costs of building an IoT infrastructure and teams in-house. It also lowers costs over time.
- Flexibility to scale – External vendors can rapidly add developer resources and expertise to match evolving project needs. This makes it easier to scale IoT initiatives without major fixed investments.
- Focus on core competencies – Automakers can stay focused on their vehicles and engineering strengths while their partners handle the IoT systems integration and services.
- Access to the latest technologies – Development partners will stay on top of emerging IoT, cloud and AI technologies as they build solutions using the latest platforms and tools.
- Risk mitigation – Experienced vendors will reduce execution risks and help avoid pitfalls when rolling out complex IoT projects with interdependent hardware, software, and services.
- Integration support – Partners help to integrate the IoT solutions within the automaker’s existing vehicle electronics, telematics systems, and IT infrastructure.
- Ongoing operations support – Vendors can provide support beyond development including managing the IoT cloud services, helpdesk, and technical support. This lightens the IT load for automakers.
Conclusion
IoT is fundamental for moving automotive technology forward and, therefore, automotive organizations are eagerly launching various IoT projects. However, it’s important to approach such initiatives with a well-thought-out plan and strategy.
By leveraging an experienced IoT developer’s expertise, an automotive organization can bring innovative connected solutions to market faster, reduce costs and stay focused on its core business. The key is to find an experienced partner that is aligned with long-term business goals.
If you’d like to learn more about the impact of IoT on automotive or want to launch an innovative project of your own, contact our experts for a free consultation.



